Ankle Examination: Difference between revisions
| (12 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{partial}} | |||
==Examination Structure== | ==Examination Structure== | ||
*Gait | *Gait | ||
| Line 12: | Line 13: | ||
***Simmonds-Thompson test | ***Simmonds-Thompson test | ||
**Tarsal tunnel | **Tarsal tunnel | ||
*[[Hip Examination|Hip]] and [[Knee Examination|Knee]] Examinations | |||
==Palpation== | ==Palpation== | ||
| Line 18: | Line 20: | ||
Bone tenderness posterior edge lateral malleolus – κ 0.75 | Bone tenderness posterior edge lateral malleolus – κ 0.75 | ||
Syndesmosis ligament palpation - sens 0.92, spec 0.29, LR+ 1.29, LR- 0.28 | Syndesmosis ligament palpation - sens 0.92, spec 0.29, LR+ 1.29, LR- 0.28 | ||
== Movement == | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|+Normal ankle motion | |||
!Motion | |||
!Range | |||
|- | |||
|Ankle dorsiflexion | |||
|0 to 20° | |||
|- | |||
|Ankle plantarflexion | |||
|0 to 50°, | |||
|- | |||
|Inversion | |||
|0 to 35° | |||
|- | |||
|Eversion | |||
|0 to 15° | |||
|} | |||
Also assess pronation and supination passively. | |||
==Special Tests== | ==Special Tests== | ||
| Line 27: | Line 49: | ||
* Triple compression test - tarsal tunnel | * Triple compression test - tarsal tunnel | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
! | ! Test !! Sensitivity !! Specificity !! +LR !! -LR !! Kappa | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Anterior Drawer|| 0.33 || 0.73 || +1.27 || -0.90 || -0.03 | | Anterior Drawer|| 0.33 || 0.73 || +1.27 || -0.90 || -0.03 | ||
| Line 43: | Line 65: | ||
| Triple Compression|| 0.86|| 1.0|| inf|| -0.99|| - | | Triple Compression|| 0.86|| 1.0|| inf|| -0.99|| - | ||
|} | |} | ||
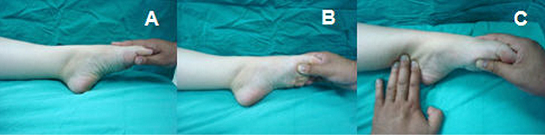
===Anterior Drawer=== | |||
[[File:anterior drawer.jpg|300px]] | |||
===Talar Tilt=== | |||
[[File:talar tilt.jpg|300px]] | |||
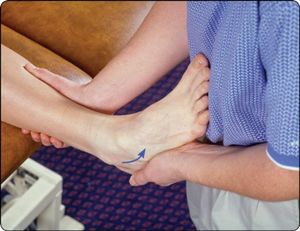
===Triple Compression Test=== | ===Triple Compression Test=== | ||
[[File:triple compression.png]] | |||
[[ | This test aims to compress the posterior tibial nerve and its branches to provoke entrapment signs of [[Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome]]. The ankle is maximally plantarflexed, and inverted. Then pressure is applied over the posterior tibial nerve. <ref>Abouelela A., Zohiery AK. The triple compression stress test for diagnosis of tarsal tunnel syndrome. Foot (Edinb). 2012 Sep;22(3):146-9. </ref> | ||
==Videos== | |||
<youtube>QiSm8rz2cmo</youtube> | |||
[https://vimeo.com/188756743 Posterior ankle examination] | |||
==Paediatric Examination of the Foot and Ankle== | |||
A consensus approach to the MSK examination in children was developed by Foster et al in 2011.<ref>{{#pmid:21954040}}</ref> The <u>underlined</u> components are those that are additional to the adult examination. The ''italicised'' components are those that the doctor should be aware of but not necessarily competent in. | |||
'''''With the patient lying supine on couch:''''' | |||
* Look at dorsal and plantar surfaces of the foot | |||
* Feel the skin temperature | |||
* Feel/palpate for peripheral pulses | |||
* Squeeze the MTPJs | |||
* Feel/palpate the mid-foot, ankle joint line and subtalar joint | |||
* Assess movement (actively and passively) at the subtalar joint (inversion and eversion), the big toe (dorsi- and plantar flexion), the ankle joint (dorsi- and plantar flexion) and mid-tarsal joints (passive rotation) | |||
* Look at the patient’s footwear | |||
* <u>Option – hypermobility, muscle power, entheses, capillaroscopy,</u> ''thigh foot angle'' | |||
'''''With the patient standing:''''' | |||
* Look at the forefoot, mid-foot (foot arch) and the hindfoot | |||
* Assess gait cycle (heel strike, stance, toe off), <u>running and turning</u> | |||
* <u>Assess muscle bulk (calves)</u> | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
[[Category:Foot | |||
[[Category:Foot and Ankle]] | |||
[[Category:Examination]] | [[Category:Examination]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:25, 3 March 2022
Examination Structure
- Gait
- Look
- Feel
- Move
- Special tests
- Syndesmosis
- Squeeze test, external rotation
- Lateral ligamentous complex
- Anterior drawer, talar tilt
- Achilles
- Simmonds-Thompson test
- Tarsal tunnel
- Syndesmosis
- Hip and Knee Examinations
Palpation
Bone tenderness base 5th MT - κ 0.78 Bone tenderness tip of medial malleolus - κ 0.66 Bone tenderness posterior edge lateral malleolus – κ 0.75 Syndesmosis ligament palpation - sens 0.92, spec 0.29, LR+ 1.29, LR- 0.28
Movement
| Motion | Range |
|---|---|
| Ankle dorsiflexion | 0 to 20° |
| Ankle plantarflexion | 0 to 50°, |
| Inversion | 0 to 35° |
| Eversion | 0 to 15° |
Also assess pronation and supination passively.
Special Tests
- Anterior drawer test – ATFL
- Talar tilt test – ATFL + CFL
- Syndesmotic squeeze or external rotation test – AITFL
- Thompson test – TA
- Triple compression test - tarsal tunnel
| Test | Sensitivity | Specificity | +LR | -LR | Kappa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anterior Drawer | 0.33 | 0.73 | +1.27 | -0.90 | -0.03 |
| Talar Tilt | 0.67 | 0.75 | +2.7 | -0.44 | - |
| Syndesmotic Squeeze | 0.3 | 0.93 | +4.6 | -0.75 | 0.5 |
| External Rotation | 0.2 | 0.85 | +1.31 | -0.94 | 0.75 |
| Thomson Test | 0.96 | 0.93 | +13.5 | -0.04 | - |
| Triple Compression | 0.86 | 1.0 | inf | -0.99 | - |
Anterior Drawer
Talar Tilt
Triple Compression Test
This test aims to compress the posterior tibial nerve and its branches to provoke entrapment signs of Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome. The ankle is maximally plantarflexed, and inverted. Then pressure is applied over the posterior tibial nerve. [1]
Videos
Paediatric Examination of the Foot and Ankle
A consensus approach to the MSK examination in children was developed by Foster et al in 2011.[2] The underlined components are those that are additional to the adult examination. The italicised components are those that the doctor should be aware of but not necessarily competent in.
With the patient lying supine on couch:
- Look at dorsal and plantar surfaces of the foot
- Feel the skin temperature
- Feel/palpate for peripheral pulses
- Squeeze the MTPJs
- Feel/palpate the mid-foot, ankle joint line and subtalar joint
- Assess movement (actively and passively) at the subtalar joint (inversion and eversion), the big toe (dorsi- and plantar flexion), the ankle joint (dorsi- and plantar flexion) and mid-tarsal joints (passive rotation)
- Look at the patient’s footwear
- Option – hypermobility, muscle power, entheses, capillaroscopy, thigh foot angle
With the patient standing:
- Look at the forefoot, mid-foot (foot arch) and the hindfoot
- Assess gait cycle (heel strike, stance, toe off), running and turning
- Assess muscle bulk (calves)
References
- ↑ Abouelela A., Zohiery AK. The triple compression stress test for diagnosis of tarsal tunnel syndrome. Foot (Edinb). 2012 Sep;22(3):146-9.
- ↑ Foster et al.. Pediatric regional examination of the musculoskeletal system: a practice- and consensus-based approach. Arthritis care & research 2011. 63:1503-10. PMID: 21954040. DOI.