Baxter's Nerve Entrapment: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Anatomy == | == Anatomy == | ||
[[File:Baxter nerve.jpg|thumb| | [[File:Baxter nerve.jpg|thumb|290x290px|Baxter nerve (Nerve to abductor digiti quinti).<ref name=":0">{{Cite journal|last=Baxter|first=D. E.|last2=Thigpen|first2=C. M.|date=1984-07|title=Heel pain--operative results|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6479759|journal=Foot & Ankle|volume=5|issue=1|pages=16–25|doi=10.1177/107110078400500103|issn=0198-0211|pmid=6479759}}</ref>]] | ||
The [[Inferior Calcaneal Nerve (Baxter Nerve)|inferior calcaneal nerve (Baxter nerve)]] is the first branch of the [[Lateral Plantar Nerve|lateral plantar nerve]], which is itself a branch of the [[Tibial Nerve|tibial nerve]]. The nerve lies in between the abductor hallucis muscle and quadratus plantae. | The [[Inferior Calcaneal Nerve (Baxter Nerve)|inferior calcaneal nerve (Baxter nerve)]] is the first branch of the [[Lateral Plantar Nerve|lateral plantar nerve]], which is itself a branch of the [[Tibial Nerve|tibial nerve]]. The nerve lies in between the abductor hallucis muscle and quadratus plantae. | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== Aetiology == | == Aetiology == | ||
There are three entrapment points:<ref | There are three entrapment points:<ref>{{Cite web|date=2012-08-01|title=Baxter's Nerve (First Branch of the Lateral Plantar Nerve) Impingement|url=https://radsource.us/baxters-nerve/|access-date=2022-04-16|website=Radsource|language=en-US}}</ref> | ||
# | # Between the deep fascia of the [[Abductor Hallucis]] and medial plantar margin of the [[Quadratus Plantae]] | ||
# More distally along the anterior aspect of the medial calcaneal tuberosity. A calcaneal plantar enthesophyte and/or soft tissue changes of plantar fasciitis may contribute to entrapment at this second location. | |||
# | |||
== Risk Factors == | == Risk Factors == | ||
[[Obesity and Chronic Pain|Obesity]], diabetes, muscle hypertrophy, hyperpronated foot, pes planus, plantar calcaneal spur, [[Plantar Fasciitis|plantar fasciitis]], [[spondyloarthritis]]. | [[Obesity and Chronic Pain|Obesity]], age, diabetes, muscle hypertrophy, hyperpronated foot, pes planus, plantar calcaneal spur, [[Plantar Fasciitis|plantar fasciitis]], [[spondyloarthritis]]. | ||
== Clinical Features == | == Clinical Features == | ||
| Line 26: | Line 23: | ||
== Investigations == | == Investigations == | ||
[[File:Baxter nerve entrapment MRI.jpeg|thumb|Coronal PD image showing fatty atrophy.<ref name=":1" />]] | [[File:Baxter nerve entrapment MRI.jpeg|thumb|Coronal PD image showing fatty atrophy.<ref name=":1">Bauones, S., Feger, J. Baxter neuropathy. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org. (accessed on 15 Apr 2022) <nowiki>https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-25994</nowiki></ref>]] | ||
On MRI in the acute phase there is decreased T1 signal intensity and increased T2 signal intensity with fat saturation in the muscles innervated by the Baxter nerve. In the chronic phase there is fatty change of the [[Abductor Digiti Minimi|abductor digiti minimi]] muscle, and occasionally the [[Flexor Digitorum Brevis]] and [[Quadratus Plantae]]. | On MRI in the acute phase there is decreased T1 signal intensity and increased T2 signal intensity with fat saturation in the muscles innervated by the Baxter nerve. In the chronic phase there is fatty change of the [[Abductor Digiti Minimi|abductor digiti minimi]] muscle, and occasionally the [[Flexor Digitorum Brevis]] and [[Quadratus Plantae]]. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
[[File:Baxter nerve injection.mp4|thumb|Baxter nerve injection.<ref>Baxter's nerve Sd. Procedure: corticosteroid injection & orthotics. Good result. @Dr_Ramon_Balius #MSKUltrasound pic.twitter.com/ED9RcmqJnz</ref>]] | The nerve can be injected with corticosteroid and/or hydrodissected under ultrasound guidance. | ||
== External Links == | |||
[https://radsource.us/baxters-nerve/ Baxter's Nerve (First Branch of the Lateral Plantar Nerve) Impingement - Radsource][[File:Baxter nerve injection.mp4|thumb|Baxter nerve injection.<ref>Baxter's nerve Sd. Procedure: corticosteroid injection & orthotics. Good result. @Dr_Ramon_Balius #MSKUltrasound pic.twitter.com/ED9RcmqJnz</ref>]] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 10:26, 16 April 2022
Baxter's nerve entrapment, also known as Baxter neuropathy, is plantar heel pain arising from compression of the inferior calcaneal nerve (Baxter nerve).
Anatomy
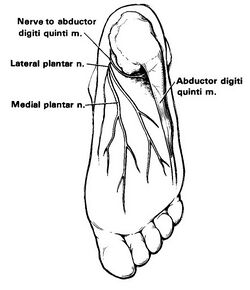
The inferior calcaneal nerve (Baxter nerve) is the first branch of the lateral plantar nerve, which is itself a branch of the tibial nerve. The nerve lies in between the abductor hallucis muscle and quadratus plantae.
The Gray's anatomy image and many other anatomy textbook images are incorrect. The Baxter nerve is quite posterior and lies very close to the calcaneus. It was named after Donald Baxter.[1]
Aetiology
There are three entrapment points:[2]
- Between the deep fascia of the Abductor Hallucis and medial plantar margin of the Quadratus Plantae
- More distally along the anterior aspect of the medial calcaneal tuberosity. A calcaneal plantar enthesophyte and/or soft tissue changes of plantar fasciitis may contribute to entrapment at this second location.
Risk Factors
Obesity, age, diabetes, muscle hypertrophy, hyperpronated foot, pes planus, plantar calcaneal spur, plantar fasciitis, spondyloarthritis.
Clinical Features
The clinical features may be similar to or coexist with plantar fasciitis. However there may be less morning pain, occasional altered sensation, and intrinsic muscle atrophy.
Differential Diagnosis
- Plantar Fasciitis
- Fat Pad Contusion
- Calcaneal fractures (traumatic and stress)
- Inferior Calcaneal (Baxter) Nerve Entrapment
- Medial Calcaneal Nerve Entrapment
- Lateral Plantar Nerve Entrapment
- Medial Plantar Nerve Entrapment
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
- Lumbar Radicular Pain
- Talar stress fracture
- Retrocalcaneal bursitis
- Spondyloarthritis
- Osteoid osteoma
- CRPS
Investigations
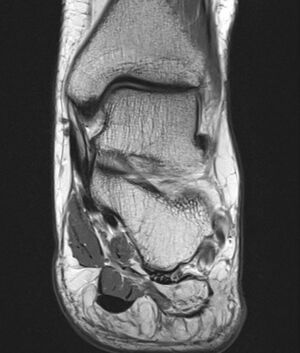
On MRI in the acute phase there is decreased T1 signal intensity and increased T2 signal intensity with fat saturation in the muscles innervated by the Baxter nerve. In the chronic phase there is fatty change of the abductor digiti minimi muscle, and occasionally the Flexor Digitorum Brevis and Quadratus Plantae.
Treatment
The nerve can be injected with corticosteroid and/or hydrodissected under ultrasound guidance.
External Links
Baxter's Nerve (First Branch of the Lateral Plantar Nerve) Impingement - Radsource
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Baxter, D. E.; Thigpen, C. M. (1984-07). "Heel pain--operative results". Foot & Ankle. 5 (1): 16–25. doi:10.1177/107110078400500103. ISSN 0198-0211. PMID 6479759. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ "Baxter's Nerve (First Branch of the Lateral Plantar Nerve) Impingement". Radsource (in English). 2012-08-01. Retrieved 2022-04-16.
- ↑ Bauones, S., Feger, J. Baxter neuropathy. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org. (accessed on 15 Apr 2022) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-25994
- ↑ Baxter's nerve Sd. Procedure: corticosteroid injection & orthotics. Good result. @Dr_Ramon_Balius #MSKUltrasound pic.twitter.com/ED9RcmqJnz

