◔
Superior Cluneal Nerve Injection
From WikiMSK
(Redirected from Cluneal Nerve Injection)
This article is a stub.
| Superior Cluneal Nerve Injection | |
|---|---|
| Indication | Cluneal Nerve Pain |
| Syringe | 10mL |
| Needle | 80mm nerve block needle |
| Steroid | optional |
| Local | doctor choice |
| Volume | ?10-15mL |
Anatomy
Indications
Contraindications
Pre-procedural Evaluation
Equipment
Technique
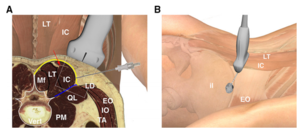
SCN block. The needle is inserted through the thoracolumbar fascia (yellow line), close to the lateral edge of iliocostalis where the posterior layer fuses with the anterior fascial layer (blue line). The red line is the lumbar intermuscular aponeurosis.
© American Society of Regional Anesthesia & Pain Medicine 2019
© American Society of Regional Anesthesia & Pain Medicine 2019
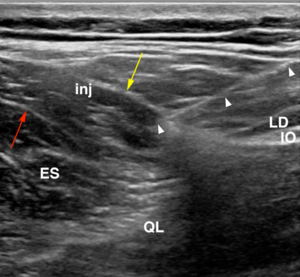
Injection can be done by landmark guided palpation based on the maximal area of tenderness, and/or by ultrasound guidance. Injections are typically done with local anaesthetic, but dextrose prolotherapy can be used[1]
Ultrasound Guided
- SCN Injection
An ultrasound guided technique for superior cluneal nerve entrapment has been developed, in a cadaveric and live human randomised study.[2]
- Position:Lateral decubitus
- Target: Subfascial layer between the thoracolumbar fascia and erector spinae to ensure injectate spread to all superior cluneal nerves.
- Probe:High frequency linear transducer.
- Identify the lateral border of the erector spinae muscle at the level of the superior margin of the iliac crest, which fuses laterally with the transverse abdominis aponeurosis.
- Trace the erector spinae caudally to the level of the iliac crest
- Keep the transducer cranial to the level of where the lumbar intermuscular aponeurosis fuses with the posterior layer of the thoracolumbar fascia.
- Insert needle lateral to medial, pierce the thoracolumbar fascia just medial to the point of fusion with the anterior layer at the lateral margin of the erector spinae.
- The erector spinae muscle and posterior layer of the thoracolumbar fascia should separate during injection, and as this happens move the needle medially.
Fluoroscopy Guided
Landmark Guided
- SCN Injection
- Position: Prone
- Palpate: posterior wings of the iliac crest, 6-7cm lateral from the midline, and mark the area. Often there is a small lipoma, and use this to guide needle placement around the lipoma.
- Advance needle perpendicularly to the marked area under contact with bone.
- Following negative aspiration inject 1mL of solution
Complications
Aftercare
Videos
See Also
External Links
References
Literature Review
- Reviews from the last 7 years: review articles, free review articles, systematic reviews, meta-analyses, NCBI Bookshelf
- Articles from all years: PubMed search, Google Scholar search.
- TRIP Database: clinical publications about evidence-based medicine.
- Other Wikis: Radiopaedia, Wikipedia Search, Wikipedia I Feel Lucky, Orthobullets,