Elbow Red Flags: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
Red flag conditions to exclude: | Red flag conditions to exclude: | ||
* fractures | |||
* tumours | {{Red flags| | ||
* infections | * fractures | ||
* inflammatory diseases | * tumours | ||
* visceral diseases. | * infections | ||
* inflammatory diseases | |||
* visceral diseases.}} | |||
Red flag conditions are rare in the elbow. | Red flag conditions are rare in the elbow. | ||
| Line 76: | Line 78: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{partial}} | |||
[[Category:Elbow & Forearm]] | [[Category:Elbow & Forearm]] | ||
[[Category:Partially complete articles]] | |||
[[Category:Red Flags]] | [[Category:Red Flags]] | ||
Revision as of 14:04, 8 April 2021
Introduction
Red flag conditions to exclude:
- fractures
- tumours
- infections
- inflammatory diseases
- visceral diseases.
Red flag conditions are rare in the elbow.
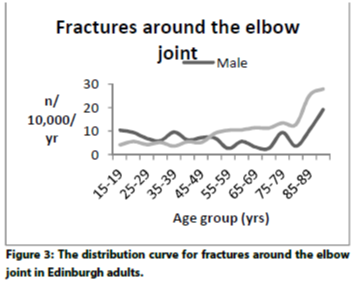
Fractures
- Is there a history of major trauma such as a fall directly on to the elbow / MVA / high speed accidents
- Is there a history of minor trauma in an individual with risk factors for osteoporosis. 11% of osteoporotic fractures involve the humerus, mostly surgical neck.
Elbow fractures make up 10% of all upper limb fractures, and 6% of all adult fractures. The incidence is 7.4 per 10,000, and is slightly higher in woman at 7.4 compared to 7.1 for men. There is an association between social deprivation and increased proximal forearm elbow fractures [1]
Malignancy
Risk factors (theoretical) are age > 50 yrs, past history of cancer, unexplained weight loss, and malaise. The clinician should also be suspicious if the patient fails to improve or is non-responsive to therapy. Suspicious examination findings are palpable soft tissue or bony deformity, and bone tenderness.
Infection
It is unclear what is the incidence of infected elbow joints and olecranon bursitis.
The Cardinal indicators for infection are:
- Fever
- Penetrating wound
- Recent procedure with needle, catheter or other instrument
- Immunosuppressed patients
- Children – hematogenous spread most common
- On examination
- Joint swelling / bursal swelling
- Bone tenderness
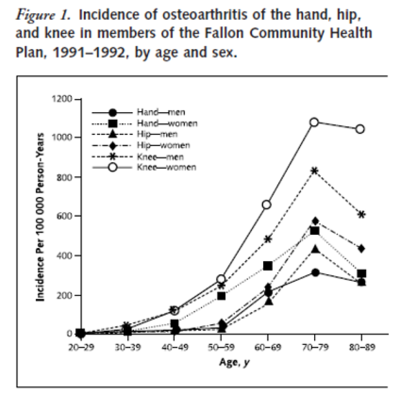
Inflammatory Arthropathies
Rheumatic disease accounts for over 7% of all conditions presenting to GP’s [2]. The most common condition is osteoarthritis at 5-10% of the population. The incidence for arthritis/arthralgia is 38.6 per 1000 population. Rheumatoid arthritis is the most important condition of the inflammatory arthritides to involve the elbow. The population incidence of rheumatoid arthritis is 2-3%.
Systemic diseases that predispose to arthropathy:
- Connective tissue disorders
- Diabetes mellitus
- Bleeding disorders
- Previous tuberculosis
- Spondyloarthropathies
- SBE, hepatitis B, rheumatic fever, HIV infection
- Vasculitides
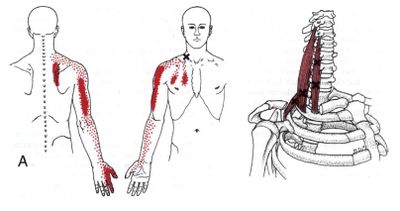
Referred Pain and Visceral Diseases
Ischaemic cardiac pain refers into the upper limb in 30% of cases Myofascial cervical spine and shoulder girdle structures can refer to the upper limb Radicular pain syndromes and other neurological syndromes can cause pain in the upper limb
Recommendations
In a patient presenting with elbow pain,
Fractures should be considered
- in a history of major trauma
- minor trauma with a background of osteoporosis
Malignancy should be considered
- Palpable mass
- History of cancer or systemic features of cancer
- No other cause found or failure to improve
Infection should be considered
- Systemic features of infection
- Local features of infection
- Bone tenderness
- History of interventional procedures