◒
Gabapentinoids
From WikiMSK
This article is still missing information.
Gabapentin![]() and pregabalin
and pregabalin![]() are together referred to as gabapentinoids. They were originally designed as antiepileptics however they have been used in a very wide range of conditions including pain conditions despite limited evidence for use.
are together referred to as gabapentinoids. They were originally designed as antiepileptics however they have been used in a very wide range of conditions including pain conditions despite limited evidence for use.
Gabapentin
- First discovered in 1970s in an attempt to create a GABA analogue
- Whilst it resembles GABA, it does not act on the GABA receptor.
- Later discovered to act on α2δ subunits of voltage-dependent calcium channels to reduce calcium influx
- Precise mechanism of analgesia unclear
- Inhibits release of excitatory neurotransmitters: glutamate, NA, substance P
- Medsafe licenced for: neuropathic pain, adjunct anti-epileptic
- Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption: Saturable transporter so delayed peak levels at higher doses. Drugs that reduce motility (e.g opiates) increase bioavailability. Peak serum conc 3 hours
- Distribution: Less lipophilic so requires active transport across the BBB
- Metabolism: minimal
- Elimination: Renal excretion, half life 5-7 hours. Dose adjustment in renal impairment
Pregabalin
- Similar to gabapentin. Binds to α2δ subunits of voltage-dependent calcium channels to reduce calcium influx
- Inhibits release of excitatory neurotransmitters: glutamate, NA, substance P
- Medsafe licenced for: neuropathic pain, adjunct anti-epileptic
- Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption: Rapid absorption after oral administration. Peak serum conc 1h
- Distribution: Less lipophilic so requires active transport across the BBB
- Metabolism: minimal, no active metabolites
- Elimination: Renal excretion, half life 6.3 hours. Dose adjustment in renal impairment
Recommended prescribing: NZF
Gabapentin
- Day 1 300mg nocte
- Day 2 300mg bd
- Day 3 300mg tds
- Then increase by 300mg every 2-3 days to max dose 3600mg daily
Pregabalin
- Initially 75mg bd
- 150mg bd after 3-7 days
- Max dose 300mg bd after further 7 days
Titrate upwards until pain relief, side effects, or max dose reached
Remember to dose adjust for renal impairment: gabapentin if <80mL/min, pregabalin if <60mL/min
Caution in pregnancy (category B1); no clear data available, use if benefits outweigh risks
Evidence
Post-herpetic neuralgia, diabetic peripheral neuropathy and fibromyalgia
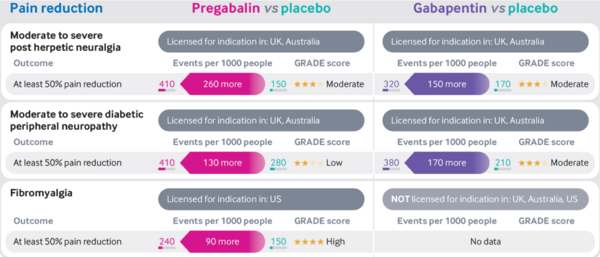
- Moderate quality evidence supports the use of gabapentinoids to improve pain in those with post-herpetic neuralgia or diabetic peripheral neuropathy compared with placebo [1] [2]
- High quality evidence supports the use of pregabalin to improve pain in those with fibromyalgia compared to placebo [3]
- The evidence for gabapentin in fibromyalgia is unclear because of the small number of trials and very low quality of evidence available [4]
- NNTs
- Moderate to severe post-herpetic neuralgia: Pregabalin 4, Gabapentin 7
- Moderate to severe diabetic peripheral neuropathy: Pregabalin 8, Gabapentin 6
- Fibromyalgia: Gabapentin 10
Low back and radicular pain
- Systematic review and meta-analysis of 7 RCTs compared gabapentin and pregabalin to placebo. Judged moderate-high quality data [5]
- Low back pain with or without lumbar radicular pain
- No difference in pain or disability at short, intermediate or long term follow up
- Lumbar radicular pain only
- No difference in pain or disability at short, intermediate or long term follow up
Other conditions
- Central neuropathic pain: Pregabalin 10 (95% CI 6-28), dose >1200mg daily
- Mixed: Pregabalin 7 (95% CI 5.4-11), dose 600mg daily
- Low quality studies showing no evidence of benefit in HIV neuropathy, neuropathic cancer pain, or polyneuropathy[6]
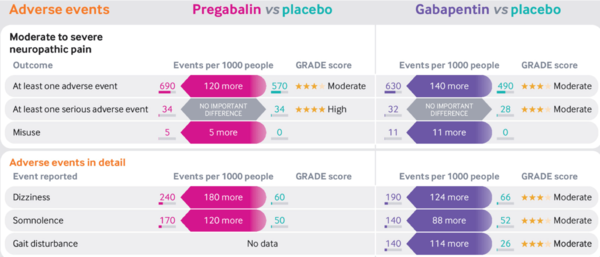
Adverse Effects
- Pregabalin and gabapentin similar profiles
- Dose-dependent
- No serious adverse effects c.f placebo
- Some common effects:
- Dizziness
- Somnolence
- Blurred vision
- Fatigue
- Weight gain and peripheral oedema
- Dry mouth
- Ataxia
- NNHs
- Moderate to severe neuropathic pain: Pregabalin 8, Gabapentin 7
Misuse and Abuse
- Supratherapeutic doses cause relaxation and euphoria.
- Taken in combination with other drugs e.g opiates, potentiates effect
- May assist with opioid withdrawal symptoms
- Those with a history of substance abuse (in particular opioids) at increased risk abuse
- UK survey: Lifetime prevalence of misuse 1.1% for gabapentin, 0.5% pregabalin
- Increasing death rate as per Finland, Sweden, Germany, UK post-mortem toxicology registers (almost all cases due to multisubstance)
- Misused gabapentinoids obtained from healthcare providers in 63% cases (UK and US study)
- In 2019, UK re-classified as scheduled class C drug (1 month prescriptions and no repeats)
- Think twice when prescribing and check indication if patient presents already on it[7]
Summary
- First line treatment for some patients with post-herpetic neuralgia and diabetic peripheral neuropathy
- Moderate to high quality evidence that not effective for low back pain or radicular pain
- Limited evidence for other conditions
References
- ↑ Derry et al.. Pregabalin for neuropathic pain in adults. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2019. 1:CD007076. PMID: 30673120. DOI. Full Text.
- ↑ Wiffen et al.. Gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain in adults. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2017. 6:CD007938. PMID: 28597471. DOI. Full Text.
- ↑ Derry et al.. Pregabalin for pain in fibromyalgia in adults. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2016. 9:CD011790. PMID: 27684492. DOI. Full Text.
- ↑ Cooper et al.. Gabapentin for fibromyalgia pain in adults. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2017. 1:CD012188. PMID: 28045473. DOI. Full Text.
- ↑ Enke et al.. Anticonvulsants in the treatment of low back pain and lumbar radicular pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. CMAJ : Canadian Medical Association journal = journal de l'Association medicale canadienne 2018. 190:E786-E793. PMID: 29970367. DOI. Full Text.
- ↑ Derry S et al. Pregabalin for neuropathic pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2019;1:CD007076. Wiffen PJ et al. Gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2017;6:CD007938
- ↑ Hägg, S et al. Current Evidence on Abuse and Misuse of Gabapentinoids. Drug Safety 2020.43, 1235–1254