◔
Hand and Wrist Examination: Difference between revisions
From WikiMSK
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 74: | Line 74: | ||
===Neurological Exam=== | ===Neurological Exam=== | ||
== Paediatric Examination == | |||
A consensus approach to the MSK examination in children was developed by Foster et al in 2011.<ref>{{#pmid:21954040}}</ref> The <u>underlined</u> components are those that are additional to the adult examination The ''italicised'' components are those that the doctor should be aware of but not necessarily competent in. | |||
* Look at the hands (palms and backs) for muscle wasting, joint swelling, skin and nail changes | |||
* Feel for radial pulse, tendon thickening and bulk of thenar and hypothenar eminences | |||
* Feel for skin temperature | |||
* Squeeze metacarpophalangeal joints (MCPJs) | |||
* Bimanually feel /palpate small joints of the hands including wrists and especially if there are swollen or painful joints or restricted movement noted) | |||
* Look and feel along ulnar border | |||
* Assess full finger extension and full finger tuck | |||
* Assess wrist flexion and extension, abduction and adduction – active and passive | |||
* Assess function: grip and pinch, picking up small object, <u>writing / drawing</u> | |||
* <u>Option – hypermobility syndromes, muscle power, capillaroscopy, peripheral nerves</u> | |||
[[Category:Examination]] | [[Category:Examination]] | ||
[[Category:Hand and Wrist]] | [[Category:Hand and Wrist]] | ||
Revision as of 21:16, 22 August 2021
This article is a stub.
Sequence
Inspection
- Expose both limbs to the elbow
- All aspects
- Don’t forget forearm or ulna aspects
- Seated, hands on pillow or desk
- Posture/alignment
- Tremor
- Swelling
- Colour
- Wasting
- Scars
Movement
- Wrist
- Observe supination/pronation rhythm as you inspect
- Flexion/extension
- Radial/ulnar deviation
- Pronation/supination
- Fingers
- Flexion/Extension
- MCPJs – 0-90°
- PIPJs – 0-110°
- DIPJs – 0-90°
- Abduction/Adduction
- Thumb
- Adduction, abduction, opposition, flexion, extension
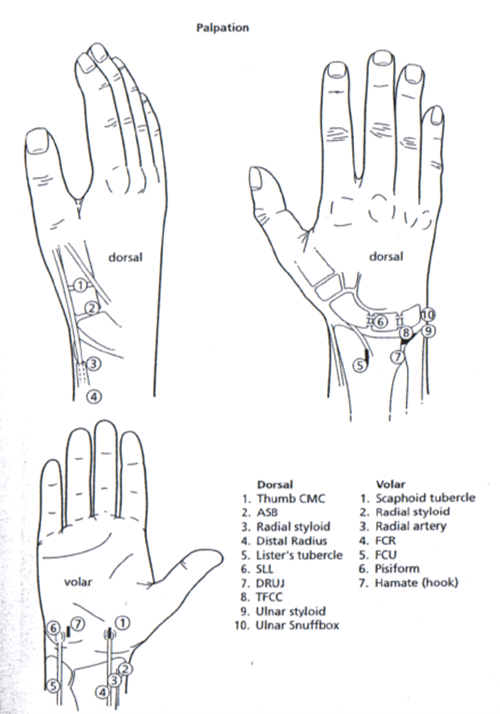
Palpation
Landmarks
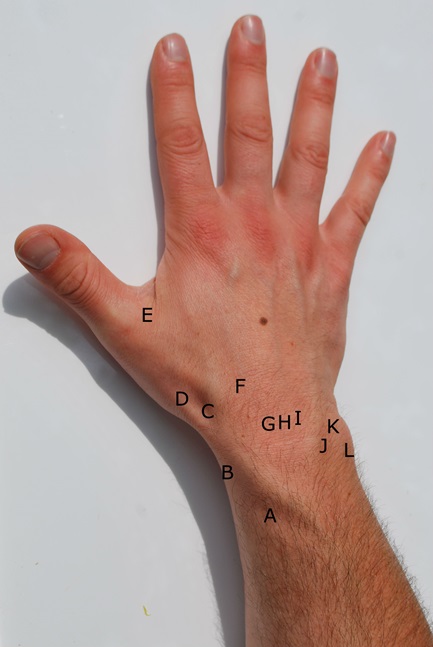
Dorsal Wrist Pain
- A = Intersection syndrome
- B = De Quervain’s tenosynovitis
- C = Scaphoid fracture / Wartenbergs syndrome (nerve entrapment)
- D = Base of thumb arthritis
- E = Ulnar collateral ligament injury
- F = Carpal boss
- G = Scapholunate ligament tear
- H = Keinbock’s disease
- I = Lunotriquetral ligament tear
- J = DRUJ (distal radioulnar joint) arthritis / instability
- K = Ulnar impaction / TFCC tear
- L = ECU dislocation / tendonitis
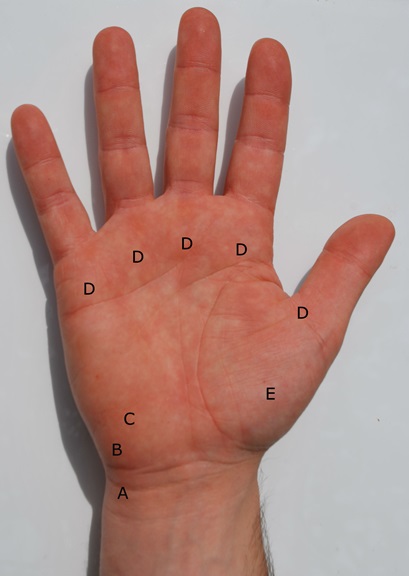
Volar Wrist Pain
- A = FCU tendonitis
- B = Pisiotriquetral arthritis / Ulnar nerve entrapment / ulnar artery thrombosis
- C = Hook of hamate fracture
- D = Trigger finger
- E = Base of thumb arthritis
Special Tests
Special Tests (depends on site of pain, ulnar, radial or mid)
- Scapholunate instability - Watson test
- DRUJ instability - Compression/ballotment test, Piano key, Drawer
- Lunotriquetral instability – lunotriquetral ballotment test
- Finkelsteins
- Radiocarpal and midcarpal drawer tests
- Ulnocarpal stress test
- ECU subluxation
- 1st CMC OA – CMC grind test, shuck test, see progressive adduction with hyperextension
Tendons
Neurological Exam
Paediatric Examination
A consensus approach to the MSK examination in children was developed by Foster et al in 2011.[1] The underlined components are those that are additional to the adult examination The italicised components are those that the doctor should be aware of but not necessarily competent in.
- Look at the hands (palms and backs) for muscle wasting, joint swelling, skin and nail changes
- Feel for radial pulse, tendon thickening and bulk of thenar and hypothenar eminences
- Feel for skin temperature
- Squeeze metacarpophalangeal joints (MCPJs)
- Bimanually feel /palpate small joints of the hands including wrists and especially if there are swollen or painful joints or restricted movement noted)
- Look and feel along ulnar border
- Assess full finger extension and full finger tuck
- Assess wrist flexion and extension, abduction and adduction – active and passive
- Assess function: grip and pinch, picking up small object, writing / drawing
- Option – hypermobility syndromes, muscle power, capillaroscopy, peripheral nerves