Lumbar Medial Branch Blocks: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "{{Procedure|image=Lumbar medial branch blocks fluoroscopy left L3-5.jpg|indication=Diagnostic test for Lumbar Zygapophysial Joint Pain|needle=22-25g 3.5 inch spinal needle...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Procedure|image=Lumbar medial branch blocks fluoroscopy left L3-5.jpg|indication=Diagnostic test for [[Lumbar Zygapophysial Joint Pain]]|needle=22-25g 3.5 inch spinal needle|local=1-4% lidocaine or 0.5-0.75% bupivacaine|volume=0.5mL over each targeted nerve | {{Authors}} | ||
{{Procedure | |||
|quality=Stub | |||
|image=Lumbar medial branch blocks fluoroscopy left L3-5.jpg | |||
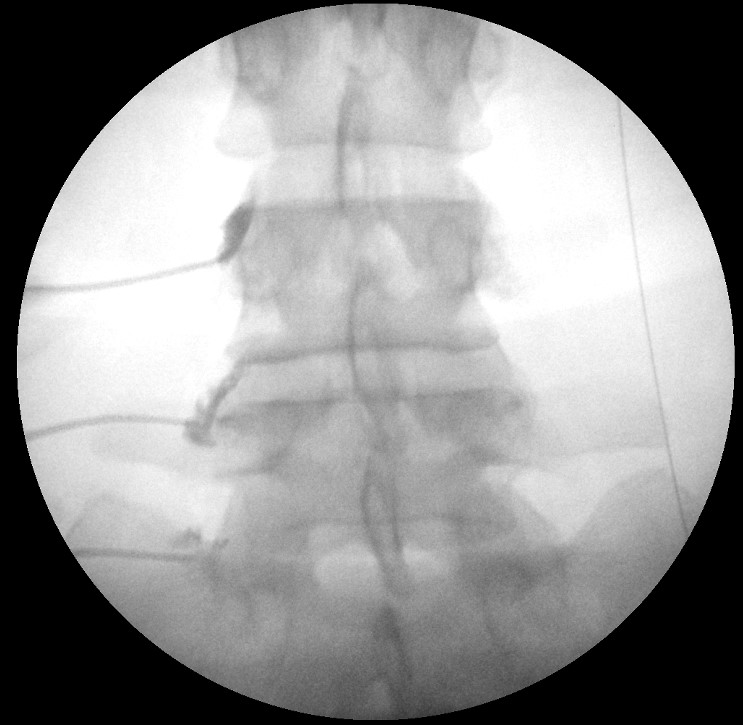
|caption=AP fluoroscopy image of left L3 and L4 medial branch and L5 dorsal ramus blocks. | |||
|indication=Diagnostic test for [[Lumbar Zygapophysial Joint Pain]] | |||
|syringe=3mL syringe | |||
|needle=22-25g 3.5 inch spinal needle | |||
|local=1-4% lidocaine or 0.5-0.75% bupivacaine | |||
|volume=0.5mL over each targeted nerve | |||
}} | |||
Controlled lumbar medial branch blocks are the only validated tool for diagnosing [[Lumbar Zygapophysial Joint Pain|lumbar zygapophysial joint pain]]. | |||
== Pre-Procedural Evaluation == | ==Pre-Procedural Evaluation== | ||
Obtain adequate consent. An emphasis should be placed on this procedure being '''a test not a treatment.''' This concept should be repeated several times and also be provided in written information. The concept can be reinforced through visual means by drawing a pain graph for the patient showing the expected response with pain going back up to baseline. Despite all this some patients may still be surprised that the pain came back after the anaesthetic wears off. | Obtain adequate consent. An emphasis should be placed on this procedure being '''a test not a treatment.''' This concept should be repeated several times and also be provided in written information. The concept can be reinforced through visual means by drawing a pain graph for the patient showing the expected response with pain going back up to baseline. Despite all this some patients may still be surprised that the pain came back after the anaesthetic wears off. | ||
| Line 10: | Line 21: | ||
Before the procedure the patient records a pain diagram, their pain ratings (worst ever experienced, worst ever for index pain, and index pain on day of procedure), and four activities that are limited by the index pain. The recording sheet has a section for recording the pain before, immediately following, and several hours after the procedure, along with an area for recording whether painful activities are restored. | Before the procedure the patient records a pain diagram, their pain ratings (worst ever experienced, worst ever for index pain, and index pain on day of procedure), and four activities that are limited by the index pain. The recording sheet has a section for recording the pain before, immediately following, and several hours after the procedure, along with an area for recording whether painful activities are restored. | ||
== Post-Procedural Evaluation == | ==Technique== | ||
===L1-L4 Medial Branches=== | |||
In the AP view the intersection of the superior articular process and the transverse process is where the medial branch passes. The mamillo-accessory ligament passes between the mamillary process on the base of the superior articular process and the accessory process on the proximal end of the transverse process. | |||
On the oblique view the target is also identified. | |||
==Post-Procedural Evaluation== | |||
[[Category:Lumbar Spine Procedures]] | [[Category:Lumbar Spine Procedures]] | ||
Revision as of 20:57, 13 April 2022
| |
| Lumbar Medial Branch Blocks | |
|---|---|
| Indication | Diagnostic test for Lumbar Zygapophysial Joint Pain |
| Syringe | 3mL syringe |
| Needle | 22-25g 3.5 inch spinal needle |
| Local | 1-4% lidocaine or 0.5-0.75% bupivacaine |
| Volume | 0.5mL over each targeted nerve |
Controlled lumbar medial branch blocks are the only validated tool for diagnosing lumbar zygapophysial joint pain.
Pre-Procedural Evaluation
Obtain adequate consent. An emphasis should be placed on this procedure being a test not a treatment. This concept should be repeated several times and also be provided in written information. The concept can be reinforced through visual means by drawing a pain graph for the patient showing the expected response with pain going back up to baseline. Despite all this some patients may still be surprised that the pain came back after the anaesthetic wears off.
Premedication is not recommended because it can interfere with the interpretation of the results. If the patient cannot tolerate the procedure without premedication due to anxiety then the anxiety should be treated first rather than proceeding to medial branch blocks.
No physiological monitoring or intravenous access is required.
Before the procedure the patient records a pain diagram, their pain ratings (worst ever experienced, worst ever for index pain, and index pain on day of procedure), and four activities that are limited by the index pain. The recording sheet has a section for recording the pain before, immediately following, and several hours after the procedure, along with an area for recording whether painful activities are restored.
Technique
L1-L4 Medial Branches
In the AP view the intersection of the superior articular process and the transverse process is where the medial branch passes. The mamillo-accessory ligament passes between the mamillary process on the base of the superior articular process and the accessory process on the proximal end of the transverse process.
On the oblique view the target is also identified.

