Peroneal Tendon Sheath Injection
| Peroneal Tendon Sheath Injection | |
|---|---|
| Indication | Peroneal Tendinopathy |
| Syringe | 3mL |
| Needle | 25-gauge 1.5-inch needle |
| Steroid | 1mL of 40mg triamcinolone. |
| Local | 1mL of 1% lidocaine |
| Volume | 2mL |
Anatomy
The peroneal tendons are located in the lateral compartment of the leg behind the lateral malleolus. Peroneus longus then divides and passes under the arch of the foot and inserts at the base of the great toe. Peroneus brevis inserts into the base of the fifth metatarsal. The division of the two tendons can be found by having the patient hold the foot in strong eversion and palpating for the V-shaped fork of the two tendons. They are the primary structures provided foot eversion. They are important active stabilisers of the ankle joint. Three are three categories of painful peroneal tendon disorders: tendinopathy, instability (subluxation and dislocation), and tears and ruptures.
Indications and Efficacy
In a study of 96 patients who had peroneal tendon sheath injections, 25% progressed to surgery. 43.7% reported 0-1 weeks of pain relief, 12.6% 2-6 weeks, 6.9% 7-12 weeks, and 36.8% greater than 12 weeks. Preinjection duration of symptoms was associated with post-injection duration of pain relief (P=.036). Patients with less than 1 year of symptoms had a median 6-12 weeks of postinjection pain relief.[1]
Contraindications
Pre-procedural Evaluation
Equipment
Technique
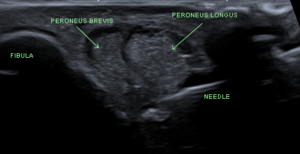
Ultrasound Guided
- Position: Lateral decubitus
- Outline distal fibula with a pen
- Clean area with alcohol, and load 1mL of 1% lidocaine and 1mL of 40mg triamcinolone.
- 25-gauge 1.5-inch needle
- High frequency probe in transverse position
- Visualise tendons running together at the level of the distal fibula
- Visualise needle during injection to confirm intrasheath, extratendinous injection.
Landmark Guided
In a study of 20 cadavers, landmark guidance was only 60% accurate, vs 100% accurate for ultrasound.[2]
- Position: Supine with foot supported in slight internal rotation
- Identify and mark the division between the two tendons
- Insert the needle perpendicularly at the division.
- Turn the needle and slide it horizontally towards the malleolus
- Inject solution into the combined tendon sheath. There should be minimal resistance.
Complications
In a study of 96 patients, there were 2 reported complications (1.8%): 1 case of self-limited sural nerve irritation and 1 of peroneus longus tear progression.[1]
Aftercare
Avoid overuse of the ankle for one week. The causative factors should be addressed where possible.
Videos
See Also
External Links
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Fram et al.. Clinical Outcomes and Complications of Peroneal Tendon Sheath Ultrasound-Guided Corticosteroid Injection. Foot & ankle international 2019. 40:888-894. PMID: 31068007. DOI.
- ↑ Muir et al.. The accuracy of ultrasound-guided and palpation-guided peroneal tendon sheath injections. American journal of physical medicine & rehabilitation 2011. 90:564-71. PMID: 21765275. DOI.
Literature Review
- Reviews from the last 7 years: review articles, free review articles, systematic reviews, meta-analyses, NCBI Bookshelf
- Articles from all years: PubMed search, Google Scholar search.
- TRIP Database: clinical publications about evidence-based medicine.
- Other Wikis: Radiopaedia, Wikipedia Search, Wikipedia I Feel Lucky, Orthobullets,