Somatic Referred Pain: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
[[File:Cervical-Radicular-Pain-Patterns.pdf]] | [[File:Cervical-Radicular-Pain-Patterns.pdf]] | ||
== Lumbar Interspinous Ligaments == | == Lumbar Interspinous Ligaments == | ||
| Line 45: | Line 44: | ||
[[File:kellgren lumbar pain.PNG|600px|Referred pain patterns from noxious stimulation of the lumbar interspinous ligaments. Kellgren 1939.]] | [[File:kellgren lumbar pain.PNG|600px|Referred pain patterns from noxious stimulation of the lumbar interspinous ligaments. Kellgren 1939.]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Cervical Spine Pain]] | ||
[[Category:Lumbar Spine Pain]] | |||
[[Category:Referred Pain]] | |||
Revision as of 06:27, 16 June 2020
Introduction
Somatic referred pain has a characteristic quality. It is deep, achy, expanding pressure, and is felt in a broad area. The location remains consistent. Patients can clearly identify the centre of pain, but find it hard to define the boundaries.
In contrast, radicular pain is shooting or lancinating, and extends along a narrow band. Neuropathic pain is burning and has sensory abnormalities. Somatic referred pain has no neurological deficit.
Inman and Saunders (1944) were the first to describe sclerotomes. They envisaged sclerotomes representing sensory innervation of skeletal tissues. They were distinct from myotomes and dermatomes. Unfortunately no anatomical basis has been found to corroborate the sclerotome. Dermatomes were originally mapped from patients with herpes zoster, and then confirmed through dorsal rhizotomy. Myotomes were mapped from patients with spinal cord injuries, and then confirmed through EMG studies. We don't know if "sclerotome patterns" are a result of central connections or peripheral segmental innervation.
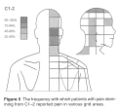
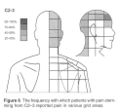
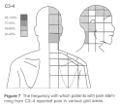
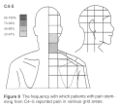
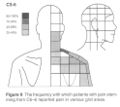
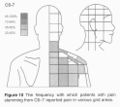
The interspinous ligaments were the first to be tested by injecting hypertonic saline. Then from the 1970s other structures were investigated. The cervical facet joints are the only pain patterns that have been shown to be fairly consistent between individuals. The source of pain from other regions cannot be easily inferred from pain maps due to high variability.
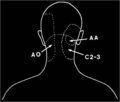
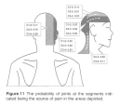
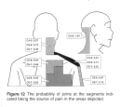
Cervical Facetogenic Pain
Cervical Pain Maps for Medial Branch Blocks
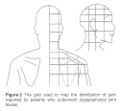
Full Image: File:Cervical Pain Maps Grid.jpg
Probabilities
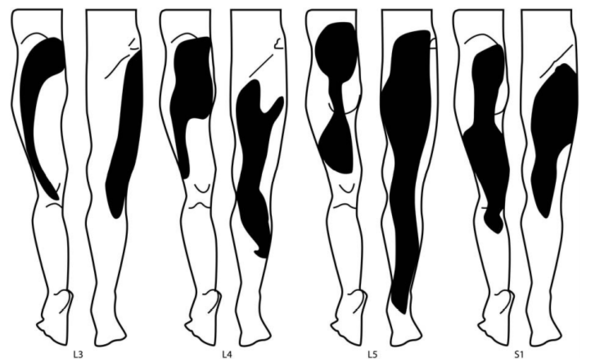
Cervical Radicular Pain
File:Cervical-Radicular-Pain-Patterns.pdf