◒
Supraorbital Nerve Injection: Difference between revisions
From WikiMSK
No edit summary |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== | {{partial}} | ||
{{procedure | |||
|image=Supraorbital and supratrochlear nerve block.png | |||
|indication=Headache disorders and laceration repair | |||
|syringe=1-3mL | |||
|needle=27-30G | |||
|local=1-3mL of anaesthetic | |||
|volume=1-3mL | |||
}} | |||
==Anatomy== | |||
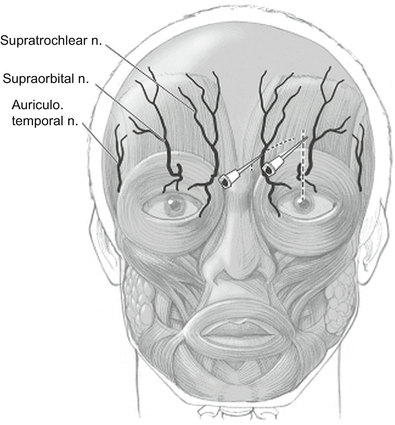
The supraorbital nerve is a branch of the terminal cutaneous branches of the frontal nerve. It runs through the supraorbital notch and innervates the upper eyelid, forehead, and anterior 1/3 of the scalp. It then ascends up the forehead. It is closely associated with the supraorbital artery medially. The supraorbital nerve is found just above the supraorbital notch. | |||
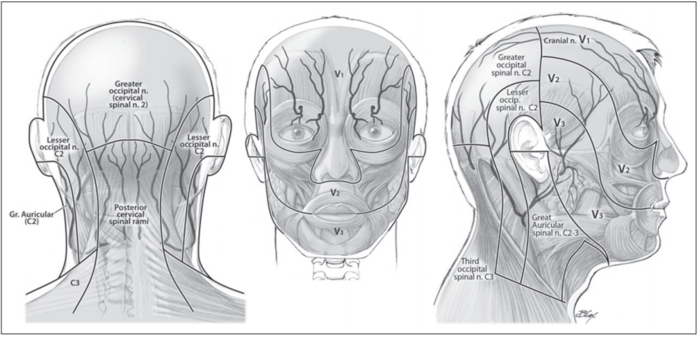
;Cranio-cervical Dermatomes.<ref>{{#pmid:23406160}}</ref> | |||
[[File:Cranial dermatomes.png|700px]] | |||
==Indications== | ==Indications== | ||
*Headache disorders | |||
*Trauma or need to perform painful procedure on area innervated by supraorbital nerve | *Trauma or need to perform painful procedure on area innervated by supraorbital nerve | ||
==Contraindications== | ==Contraindications== | ||
*Infection overlying injection site | *Infection overlying injection site | ||
| Line 13: | Line 26: | ||
==Equipment Needed== | ==Equipment Needed== | ||
*local anesthesia | *[[Local Anaesthetics|local anesthesia]] | ||
**lidocaine 2% (lasts 30-60 minutes or longer if given with epinephrine, rapid onset of 4-6 minutes) | **[[lidocaine]] 2% (lasts 30-60 minutes or longer if given with epinephrine, rapid onset of 4-6 minutes) | ||
**Bupivacaine 0.5% (lasts 2-4 hours, slowest in onset) | **[[Bupivacaine]] 0.5% (lasts 2-4 hours, slowest in onset) | ||
*18 gauge needle to draw up anesthetic | *18 gauge needle to draw up anesthetic | ||
*1.5 inch 25 or 27 gauge needle | *1.5 inch 25 or 27 gauge needle | ||
| Line 24: | Line 37: | ||
==Procedure== | ==Procedure== | ||
*Obtain informed consent | |||
*Place patient in supine position or seated | |||
*Draw up 2-5cc of anesthetic into syringe | |||
*Palpate the supraorbital notch over the medial aspect of the supraorbital ridge | |||
*Prep area | |||
*Advance the needle towards foramen to a depth of 4-5mm | |||
*Aspirate, and if no blood, inject 1-3 cc of anesthetic slowly | |||
*Massage area for 10-15 seconds | |||
*If block is unsuccessful, inject a line of anesthetic solution along the orbital rim laterally to medially to block all branches of the ophthalmic nerve | |||
==Complications== | ==Complications== | ||
| Line 41: | Line 54: | ||
*Allergic reaction to anesthetic | *Allergic reaction to anesthetic | ||
*Damage to nerves/vessels | *Damage to nerves/vessels | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| Line 49: | Line 59: | ||
*Amsterdam J and Kilgore K. Regional Anesthesia of the Head and Neck. In: Roberts and Hedges' Clinical Procedures in Emergency Medicine. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2014 | *Amsterdam J and Kilgore K. Regional Anesthesia of the Head and Neck. In: Roberts and Hedges' Clinical Procedures in Emergency Medicine. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2014 | ||
[[Category:Head | [[Category:Head and Jaw Procedures]] | ||
[[Category:Infoboxes]] | |||
[[Category:Partially complete articles]] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:31, 4 March 2022
This article is still missing information.
| |
| Supraorbital Nerve Injection | |
|---|---|
| Indication | Headache disorders and laceration repair |
| Syringe | 1-3mL |
| Needle | 27-30G |
| Local | 1-3mL of anaesthetic |
| Volume | 1-3mL |
Anatomy
The supraorbital nerve is a branch of the terminal cutaneous branches of the frontal nerve. It runs through the supraorbital notch and innervates the upper eyelid, forehead, and anterior 1/3 of the scalp. It then ascends up the forehead. It is closely associated with the supraorbital artery medially. The supraorbital nerve is found just above the supraorbital notch.
- Cranio-cervical Dermatomes.[1]
Indications
- Headache disorders
- Trauma or need to perform painful procedure on area innervated by supraorbital nerve
Contraindications
- Infection overlying injection site
- Previous allergic reaction to local anesthetic
- Uncooperative patient
- Distortion of anatomical landmarks
Equipment Needed
- local anesthesia
- lidocaine 2% (lasts 30-60 minutes or longer if given with epinephrine, rapid onset of 4-6 minutes)
- Bupivacaine 0.5% (lasts 2-4 hours, slowest in onset)
- 18 gauge needle to draw up anesthetic
- 1.5 inch 25 or 27 gauge needle
- 3-5cc syringe
- gauze pads
- gloves
- betadine/chlorhexidine
Procedure
- Obtain informed consent
- Place patient in supine position or seated
- Draw up 2-5cc of anesthetic into syringe
- Palpate the supraorbital notch over the medial aspect of the supraorbital ridge
- Prep area
- Advance the needle towards foramen to a depth of 4-5mm
- Aspirate, and if no blood, inject 1-3 cc of anesthetic slowly
- Massage area for 10-15 seconds
- If block is unsuccessful, inject a line of anesthetic solution along the orbital rim laterally to medially to block all branches of the ophthalmic nerve
Complications
- Bleeding/hematoma
- Infection
- Pain
- Swelling of face/eyelid
- Allergic reaction to anesthetic
- Damage to nerves/vessels
References
- Amsterdam J and Kilgore K. Regional Anesthesia of the Head and Neck. In: Roberts and Hedges' Clinical Procedures in Emergency Medicine. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2014