File:Aggrecan function.png
Aggrecan_function.png (567 × 295 pixels, file size: 76 KB, MIME type: image/png)
Summary
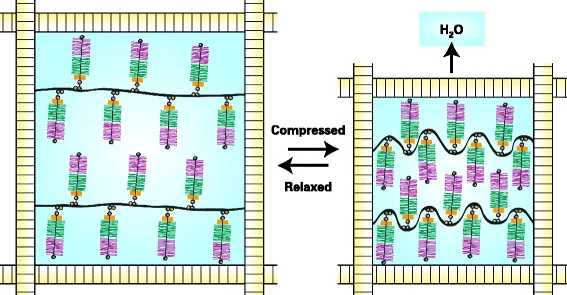
Proteoglycan aggregates are depicted as being entrapped by collagen fibrils. In the relaxed state the aggregates swell as the anionic chondroitin sulfate and keratan sulfate chains draw water into the tissue until an equilibrium is attained in which swelling is balance by tensile forces in the collagen fibrils. Under compression, water is displaced and the chondroitin sulfate and keratan sulfate chains are brought into closer proximity, so increasing their swelling potential and balancing the applied load. The increased swelling potential is dissipated upon removal of the load as the original equilibrium is restored.
Roughley, P.J., Mort, J.S. The role of aggrecan in normal and osteoarthritic cartilage. J EXP ORTOP 1, 8 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40634-014-0008-7
Licencing
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 16:39, 31 July 2021 |  | 567 × 295 (76 KB) | Jeremy (talk | contribs) | Proteoglycan aggregates are depicted as being entrapped by collagen fibrils. In the relaxed state the aggregates swell as the anionic chondroitin sulfate and keratan sulfate chains draw water into the tissue until an equilibrium is attained in which swelling is balance by tensile forces in the collagen fibrils. Under compression, water is displaced and the chondroitin sulfate and keratan sulfate chains are brought into closer proximity, so increasing their swelling potential and balancing the... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: