Acute Neck Pain: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
*Iatrogenic: Recent surgery, catheterisation, venipuncture, manipulation | *Iatrogenic: Recent surgery, catheterisation, venipuncture, manipulation | ||
*Neurological: Symptoms/signs especially of upper motor neuron pathology, vomiting | *Neurological: Symptoms/signs especially of upper motor neuron pathology, vomiting | ||
*Genitourinary/Reproductive: UTI, haematuria, retention, uterine, breast | *Genitourinary/Reproductive: UTI, haematuria, retention, uterine, breast | ||
*Endocrine: Corticosteroids, diabetes, hyperparathyroid | *Endocrine: Corticosteroids, diabetes, hyperparathyroid | ||
*Gastrointestinal: Dysphagia | *Gastrointestinal: Dysphagia | ||
*Integumentary: Infections, rashes | *Integumentary: Infections, rashes | ||
*Cardiorespiratory: Cough, haemoptysis, chest pain, shortness of breath, diaphoresis, ripping/tearing sensation (dissection) | *Cardiorespiratory: Cough, haemoptysis, chest pain, shortness of breath, diaphoresis, ripping/tearing sensation (dissection), risk factors, anticoagulants | ||
*Rheumatological: History of rheumatoid arthritis (atlanto-axial disruption) | *Rheumatological: History of rheumatoid arthritis (atlanto-axial disruption) | ||
*Awkward posture (atlantoaxial rotatory subluxation in children) | *Awkward posture (atlantoaxial rotatory subluxation in children) | ||
Revision as of 15:11, 24 May 2021
Clinical Assessment
- Significant trauma (eg. fall in osteoporotic patient, motor vehicle accident)
- Infective: (eg. fever, meningism, immunosuppression, intravenous drug use, exotic exposure, recent overseas travel)
- Constitutional: (eg. fevers, weight loss, anorexia, past or current history of malignancy)
- Iatrogenic: Recent surgery, catheterisation, venipuncture, manipulation
- Neurological: Symptoms/signs especially of upper motor neuron pathology, vomiting
- Genitourinary/Reproductive: UTI, haematuria, retention, uterine, breast
- Endocrine: Corticosteroids, diabetes, hyperparathyroid
- Gastrointestinal: Dysphagia
- Integumentary: Infections, rashes
- Cardiorespiratory: Cough, haemoptysis, chest pain, shortness of breath, diaphoresis, ripping/tearing sensation (dissection), risk factors, anticoagulants
- Rheumatological: History of rheumatoid arthritis (atlanto-axial disruption)
- Awkward posture (atlantoaxial rotatory subluxation in children)
It is rarely possible to establish a patho-anatomic diagnosis in acute neck pain, and so the diagnostic process is one of exclusion.
The first step is evaluating whether the patient has neurological symptoms or signs. If they do then they should be assessed under a neurological disorders framework rather than an acute neck pain framework as the neurological disorder takes precedence. Neurological disorders include spinal cord injury, myelopathy, and radiculopathy.
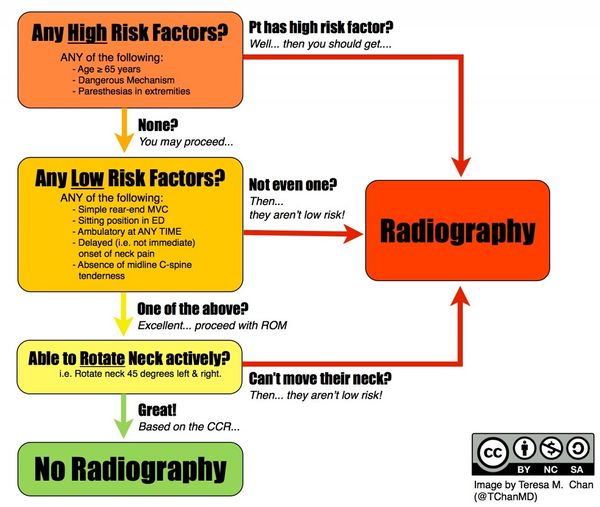
In the event of trauma, the Canadian C-spine rule should be used, and any fracture managed as appropriate.
The practitioner should remain vigilant to new clues that invites revisiting the diagnosis. Vigilance includes revisiting red flag symptoms and noting any new symptoms or signs.
Diagnosis
For patients with no history of injury the diagnosis used by the Australian Acute Musculoskeletal Guidelines is "idiopathic neck pain," while for those with neck pain following a motor vehicle accident the diagnosis is "whiplash-associated neck pain." For ACC medicolegal purposes the coding that should be used is normally "cervical sprain," but this is not a meaningful label in a medical sense as it lacks legitimacy as a diagnosis.
Management
Passive Treatment
Passive treatment is avoided. It is not effective, especially when compared to other methods. Passive management assumes that a specific diagnosis has been made, and that passive treatment will rectify said diagnosis. However no conventional examination or investigation can identify the pathology and no conventional treatment can target or resolve any specific cause of pain
Explanation and Reassurance
These often go together. Elicit the patient's ideas and concerns. Gently correct false beliefs and address any fears about serious causes or about the prognosis. A clinical assessment can effectively rule out sinister causes and so the clinician can provide reassurance based on sound evidence. The patient many not have any specific concerns or fears. Regardless the clinician should fully reassure the patient that serious causes of neck pain are rare and can be recognised on clinical assessment, and common causes are not threatening and have a good prognosis. The clinician should be truthful that in the majority of cases no one knows what causes the pain, that it is probably something simple like a sprain or sore muscles, but that there is no simple way to make an exact diagnosis. Explain that even without treatment most patients recover, and that the most effective treatment is a tincture of time. However offer other measures as below to help the process along.
Activation
Encourage the patient to maintain activity as near to normal as possible. This is critical for preventing disability. Identify any barriers to achieving this, and be prepared to suggest alternative ways of maintaining activity levels if pain impedes this. Reassure the patient that there is no injury that will be worsened by resuming activity, and no injury that requires rest. Explain that rest can leads to stiffness and that the neck should be allowed to heal in a way that allows normal function. Resuming activities reminds the neck what is expected of it.
In some cases there will need to be goal setting in that the patient should start with a short time engaged in activity and gradually progress the length of engagement. Other interventions may be used to reduce pain to allow activation. There may need to be some discussions around ergonomics, although there is no particular rule. For example if the patient struggles to turn their head while driving encourage the use of mirrors. If hanging up the washing is problematic, then recommend that the patient hang the washing down by lowering the clothes line or standing on a stool.
Simple Exercises
Exercises for keeping the neck moving may be the single most effective measure for treatment of acute neck pain. They encourage resumption of normal activities, they have a therapeutic measure, and they are an active rather than passive modality. Patients are empowered to be the vehicles for their own recovery, and treatment can be applied when convenient. The patient should engage in the exercises at certain times of the day. Timing can be attached to other activities such as meal times, getting up in the morning, and going to bed at night. The objective is to increase and maintain mobility rather than strengthening the muscles or treating a specific lesion. Follow up can be offered to check compliance and understanding.
There are a couple of New Zealand publications that can be helpful
- McKenzie RA. Treat your own Neck. Spinal Publications, Waikanae, New Zealand, 1983.
- Mulligan B. Self treatments for back, neck and limbs. Plane View Services, Wellington, 2012.
Alternatively if the clinician does not have sufficient knowledge or experience to teach exercises, then they may wish to refer them to a colleague or allied health provider. The referral should be for active treatment modalities rather than passive therapy.
Clinical Review
Early review should be offered if the patient is distressed. And if not then review may be warranted following a week or so, however if they are recovering then this may not be required. There may be financial barriers to review. At review check understanding and compliance and reinforce recommendations. The patient may not be recovering due to lack of understanding.
If the prescribed interventions are not effective at all or are not sufficiently effective then consider multimodal therapy. Multimodal therapy is a combination of exercises and manual therapy guided by a therapist.
There may be other barriers to recovery such as personal, social, or occupational barriers. There may be barriers that can be addressed for example by referral to a psychologist or occupational therapist - however there may be financial barriers.
The patient and practitioner should persist with the recommended interventions for two months. Patients will usually recover in this period if they are going to do so. The patient may be showing significant signs of recovery and so in that case it may be wise to persist with the interventions. At three months they are classified as having chronic pain, and so between the two to three month mark the practitioner should consider organising onward referral to allow timely assessment.
Analgesia
There is no evidence that any specific analgesic is effective for acute neck pain. The Australian Acute Musculoskeletal Pain Guidelines recommend the use of paracetamol, but this is based on consensus. NSAIDs have not been shown to be more effective than paracetamol, and compound analgesics (paracetamol plus codeine) are only marginally better than paracetamol alone. Opioids are not generally recommended.
Prognosis
Bibliography
- Bogduk, Nikolai, and Brian McGuirk. Management of acute and chronic neck pain : an evidence-based approach. Edinburgh New York: Elsevier, 2006.