◒
De Quervain Injection: Difference between revisions
From WikiMSK
(Created page with "{{stub}} {{procedure |indication=De Quervain Injection |syringe=1mL |needle=25G 16mm |steroid=10-20mg triamcinolone |local=0.75mL 2% lidocaine |volume=1mL }} <youtube>Y8BSLv...") |
|||
| (36 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ | {{partial}} | ||
{{procedure | {{procedure | ||
|indication=De Quervain | |indication=[[De Quervain Tendinopathy]] | ||
|syringe=1mL | |syringe=1mL | ||
|needle=25G 16mm | |needle=25G 16mm | ||
|steroid= | |steroid=0.5mL 20mg triamcinolone | ||
|local=0. | |local=0.5mL 1% lidocaine | ||
|volume=1mL | |volume=1mL | ||
}} | }} | ||
==Background== | |||
Injection for [[De Quervain Tendinopathy]]. | |||
==Anatomy== | |||
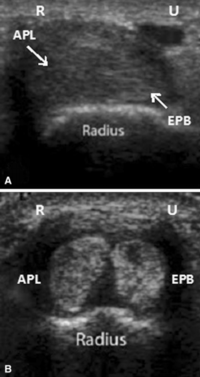
[[File:De Quervain Compartments.PNG|200px|thumb|A. One compartment.<br/>B. Two subcompartments<br/>From McDermott et al 2012<ref>McDermott JD, Ilyas AM, Nazarian LN, Leinberry CF. Ultrasound-guided injections for de Quervain's tenosynovitis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(7):1925-1931. doi:10.1007/s11999-012-2369-5</ref>]] | |||
*The APL and EPB usually run together in the first dorsal compartment. | |||
*The tendons can often be seen with the thumb held in resisted extension. | |||
*They can also be palpated at the base of the 1st metacarpal. | |||
*Anatomic variation: septum with two sub compartments (24-76% in cadaver studies). Failure can occur if failure to inject into compartment or only one sub compartment. | |||
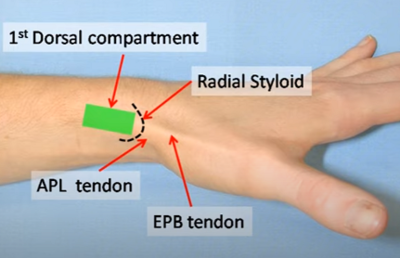
[[File:First Dorsal Compartment.PNG|400px]] | |||
==Indications== | |||
==Contraindications== | |||
==Technique== | |||
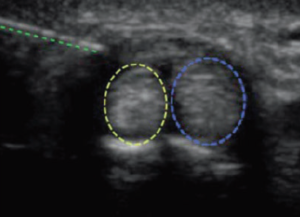
[[File:De Quervain Ultrasound Injection.PNG|300px|thumb|Long axis injection. From left to right: needle, EPB, APL.]] | |||
*Ultrasound guided is preferred with greater clinical improvement, and allows the identification of subcompartment anatomical variation <ref>McDermott JD, Ilyas AM, Nazarian LN, et al. Ultrasound-guided injections for de Quervain's tenosynovitis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470:1925–31.</ref><ref>Jeyapalan K, Choudhary S. Ultrasound-guided injection of triamcinolone | |||
and bupivacaine in the management of de Quervain’s disease. Skelet Radiol. 2009;38:1099–103.</ref><ref>Zingas C, Failla JM, Van Holsbeeck M. Injection accuracy and clinical | |||
relief of de Quervain’s tendinitis. J Hand Surg Am. 1998;23:89</ref> | |||
*Position: Ulnar side of hand resting on surface with thumbheld in slight flexion | |||
===Non-Ultrasound Guided=== | |||
*Identify: Radial styloid, the APB and EPL tendons, and the gap between them. | |||
*Injection site | |||
** Usual site: is between 5-10mm proximal to the tip of the radial styloid, between the two tendons, through the retinaculum, within the sheath. | |||
** Alternative site in very thin patients: inject distal to the retinaculum, 5mm distal to the radial styloid (due to limited subcutaneous tissue), then advance the needle proximally while injecting | |||
*Insert needle perpendicularly into the gap then slide proximally between the tendons (needle going distal to proximal) | |||
*Inject solution as a bolus | |||
===Ultrasound Guided=== | |||
* Preparation: Stand off gel recommended | |||
* Identify: APL and APB tendons in sagittal, retinaculum, radial styloid in transverse | |||
* Optional: initial infiltration of lidocaine. | |||
* Axis: Can be done long axis or short axis. Transverse view is best with the needle entering the sheath while in plan with the transducer. | |||
* Direction: Dorsal to palmar direction, at a site free of superficial veins and the superficial branch of the radial nerve | |||
* Injection | |||
**One sheath: deposit at one location in the sheath | |||
**Two sheaths: Pierce the septum between the sheaths. Deposit half around the APL, then draw back and deposit the remaining half around the EPB | |||
==Complications== | |||
*Subcutaneous fat atrophy, particularly noticeable in dark skinned thin women. This may be permanent but generally resolves within 3 months. The risk can be reduced by using hydrocortisone. | |||
*Trauma to superficial radial nerve | |||
==Aftercare== | |||
Rest hand for one week with taping. Avoid provoking activities and start a graded load programme. | |||
==External Resources== | |||
<youtube>Y8BSLvsyRTg</youtube> | <youtube>Y8BSLvsyRTg</youtube> | ||
[[Category:Hand | {{PDF|McDermott2012 Ultrasound guided de Quervain injection.pdf|Ultrasound guided de Quervain Injection - McDermott 2012}} | ||
[[Category: | |||
==References== | |||
<references/> | |||
{{Reliable sources}} | |||
[[Category:Hand and Wrist Procedures]] | |||
[[Category:Infoboxes]] | |||
[[Category:Partially complete articles]] | |||
Latest revision as of 14:21, 16 March 2022
This article is still missing information.
| De Quervain Injection | |
|---|---|
| Indication | De Quervain Tendinopathy |
| Syringe | 1mL |
| Needle | 25G 16mm |
| Steroid | 0.5mL 20mg triamcinolone |
| Local | 0.5mL 1% lidocaine |
| Volume | 1mL |
Background
Injection for De Quervain Tendinopathy.
Anatomy
- The APL and EPB usually run together in the first dorsal compartment.
- The tendons can often be seen with the thumb held in resisted extension.
- They can also be palpated at the base of the 1st metacarpal.
- Anatomic variation: septum with two sub compartments (24-76% in cadaver studies). Failure can occur if failure to inject into compartment or only one sub compartment.
Indications
Contraindications
Technique
- Ultrasound guided is preferred with greater clinical improvement, and allows the identification of subcompartment anatomical variation [2][3][4]
- Position: Ulnar side of hand resting on surface with thumbheld in slight flexion
Non-Ultrasound Guided
- Identify: Radial styloid, the APB and EPL tendons, and the gap between them.
- Injection site
- Usual site: is between 5-10mm proximal to the tip of the radial styloid, between the two tendons, through the retinaculum, within the sheath.
- Alternative site in very thin patients: inject distal to the retinaculum, 5mm distal to the radial styloid (due to limited subcutaneous tissue), then advance the needle proximally while injecting
- Insert needle perpendicularly into the gap then slide proximally between the tendons (needle going distal to proximal)
- Inject solution as a bolus
Ultrasound Guided
- Preparation: Stand off gel recommended
- Identify: APL and APB tendons in sagittal, retinaculum, radial styloid in transverse
- Optional: initial infiltration of lidocaine.
- Axis: Can be done long axis or short axis. Transverse view is best with the needle entering the sheath while in plan with the transducer.
- Direction: Dorsal to palmar direction, at a site free of superficial veins and the superficial branch of the radial nerve
- Injection
- One sheath: deposit at one location in the sheath
- Two sheaths: Pierce the septum between the sheaths. Deposit half around the APL, then draw back and deposit the remaining half around the EPB
Complications
- Subcutaneous fat atrophy, particularly noticeable in dark skinned thin women. This may be permanent but generally resolves within 3 months. The risk can be reduced by using hydrocortisone.
- Trauma to superficial radial nerve
Aftercare
Rest hand for one week with taping. Avoid provoking activities and start a graded load programme.
External Resources
References
- ↑ McDermott JD, Ilyas AM, Nazarian LN, Leinberry CF. Ultrasound-guided injections for de Quervain's tenosynovitis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(7):1925-1931. doi:10.1007/s11999-012-2369-5
- ↑ McDermott JD, Ilyas AM, Nazarian LN, et al. Ultrasound-guided injections for de Quervain's tenosynovitis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470:1925–31.
- ↑ Jeyapalan K, Choudhary S. Ultrasound-guided injection of triamcinolone and bupivacaine in the management of de Quervain’s disease. Skelet Radiol. 2009;38:1099–103.
- ↑ Zingas C, Failla JM, Van Holsbeeck M. Injection accuracy and clinical relief of de Quervain’s tendinitis. J Hand Surg Am. 1998;23:89
Literature Review
- Reviews from the last 7 years: review articles, free review articles, systematic reviews, meta-analyses, NCBI Bookshelf
- Articles from all years: PubMed search, Google Scholar search.
- TRIP Database: clinical publications about evidence-based medicine.
- Other Wikis: Radiopaedia, Wikipedia Search, Wikipedia I Feel Lucky, Orthobullets,