File:Sodium channel alpha subunit.jpg
Sodium_channel_alpha_subunit.jpg (717 × 470 pixels, file size: 50 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
Summary
Li ZM, Chen LX, Li H. Voltage-gated Sodium Channels and Blockers: An Overview and Where Will They Go? Curr Med Sci. 2019 Dec;39(6):863-873. doi: 10.1007/s11596-019-2117-0. Epub 2019 Dec 16. Erratum in: Curr Med Sci. 2020 Dec;40(6):1206. PMID: 31845216.
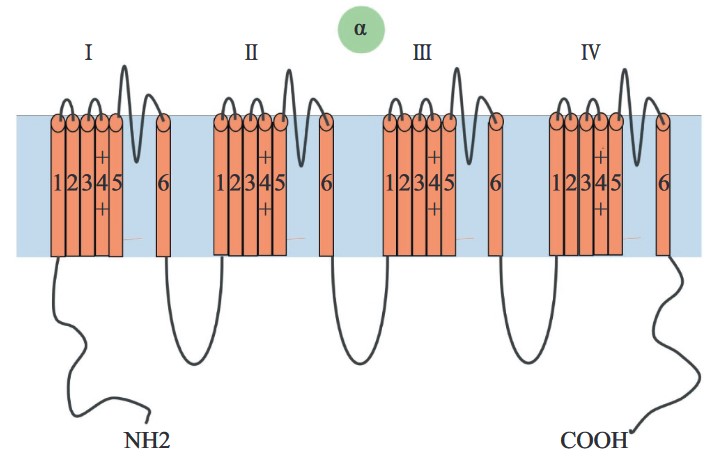
Voltage-gated sodium (Nav) channel α-subunit topology The α-subunit contains four homologous domains (I–IV) connected by intracellular linkers, each developed by α-helical transmembrane segments (S1–S6). Voltage- sensing domain (VSD) is constituted within S1–S4, which control the gating. The fourth hydrophobic segment, S4, in each domain contains positively charged amino acids (arginine or lysine) and functions as voltage sensors. Segments S5, S6, and the connecting pore-loops form the channel pore. The intracellular loop between domain III and domain IV contains the IFM (isoleucine, phenylalanine, and methionine) domain required for channel inactivation.
Licencing
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 18:04, 19 May 2023 |  | 717 × 470 (50 KB) | Jeremy (talk | contribs) | Li ZM, Chen LX, Li H. Voltage-gated Sodium Channels and Blockers: An Overview and Where Will They Go? Curr Med Sci. 2019 Dec;39(6):863-873. doi: 10.1007/s11596-019-2117-0. Epub 2019 Dec 16. Erratum in: Curr Med Sci. 2020 Dec;40(6):1206. PMID: 31845216. Voltage-gated sodium (Nav) channel α-subunit topology The α-subunit contains four homologous domains (I–IV) connected by intracellular linkers, each developed by α-helical transmembrane segments (S1–S6). Voltage- sensing domain (VSD) is consti... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: