◒
Gabapentinoids: Difference between revisions
From WikiMSK
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{partial}} | |||
==Gabapentin== | ==Gabapentin== | ||
* First discovered in 1970s in an attempt to create a GABA analogue | * First discovered in 1970s in an attempt to create a GABA analogue | ||
| Line 4: | Line 5: | ||
* Later discovered to act on α2δ subunits of voltage-dependent calcium channels to reduce calcium influx | * Later discovered to act on α2δ subunits of voltage-dependent calcium channels to reduce calcium influx | ||
** Precise mechanism of analgesia unclear | ** Precise mechanism of analgesia unclear | ||
* Inhibits release of excitatory neurotransmitters: glutamate, NA, substance P | * Inhibits release of excitatory neurotransmitters: glutamate, NA, substance P | ||
* Medsafe licenced for: neuropathic pain, adjunct anti-epileptic | * Medsafe licenced for: neuropathic pain, adjunct anti-epileptic | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
==Pregabalin== | ==Pregabalin== | ||
* Similar to gabapentin. Binds to α2δ subunits of voltage-dependent calcium channels to reduce calcium influx | * Similar to gabapentin. Binds to α2δ subunits of voltage-dependent calcium channels to reduce calcium influx | ||
** Inhibits release of excitatory neurotransmitters: glutamate, NA, substance P | ** Inhibits release of excitatory neurotransmitters: glutamate, NA, substance P | ||
| Line 23: | Line 22: | ||
** Metabolism: minimal, no active metabolites | ** Metabolism: minimal, no active metabolites | ||
** Elimination: Renal excretion, half life 6.3 hours. Dose adjustment in renal impairment | ** Elimination: Renal excretion, half life 6.3 hours. Dose adjustment in renal impairment | ||
==Recommended prescribing: NZF== | ==Recommended prescribing: NZF== | ||
'''Gabapentin''' | '''Gabapentin''' | ||
| Line 56: | Line 53: | ||
** Moderate to severe diabetic peripheral neuropathy: Pregabalin 8, Gabapentin 6 | ** Moderate to severe diabetic peripheral neuropathy: Pregabalin 8, Gabapentin 6 | ||
** Fibromyalgia: Gabapentin 10 | ** Fibromyalgia: Gabapentin 10 | ||
[[File:Gabapentinoids vs placebo pain infographic Mathieson.png|600px]] | |||
'''Low back and radicular pain''' | '''Low back and radicular pain''' | ||
| Line 66: | Line 63: | ||
** No difference in pain or disability at short, intermediate or long term follow up | ** No difference in pain or disability at short, intermediate or long term follow up | ||
==Adverse Effects== | |||
*Pregabalin and gabapentin similar profiles | |||
*Dose-dependent | |||
*No serious adverse effects c.f placebo | |||
*Some common effects: | |||
**Dizziness | |||
**Somnolence | |||
**Blurred vision | |||
**Fatigue | |||
**Weight gain and peripheral oedema | |||
**Dry mouth | |||
**Ataxia | |||
* NNHs | |||
** Moderate to severe neuropathic pain: Pregabalin 8, Gabapentin 7 | |||
[[File:Gabapentinoids vs placebo adverse effects infographic Mathieson.png|600px]] | [[File:Gabapentinoids vs placebo adverse effects infographic Mathieson.png|600px]] | ||
==Misuse and Abuse== | |||
*Supratherapeutic doses cause relaxation and euphoria. | |||
**Taken in combination with other drugs e.g opiates, potentiates effect | |||
**May assist with opioid withdrawal symptoms | |||
*Those with a history of substance abuse (in particular opioids) at increased risk abuse | |||
*UK survey: Lifetime prevalence of misuse 1.1% for gabapentin, 0.5% pregabalin | |||
*Increasing death rate as per Finland, Sweden, Germany, UK post-mortem toxicology registers (almost all cases due to multisubstance) | |||
*Misused gabapentinoids obtained from healthcare providers in 63% cases (UK and US study) | |||
*In 2019, UK re-classified as scheduled class C drug (1 month prescriptions and no repeats) | |||
*Think twice when prescribing and check indication if patient presents already on it<ref>Hägg, S et al. Current Evidence on Abuse and Misuse of Gabapentinoids. Drug Safety 2020.43, 1235–1254</ref> | |||
==Summary== | |||
*First line treatment for some patients with post-herpetic neuralgia and diabetic peripheral neuropathy | |||
*Moderate to high quality evidence that not effective for low back pain or radicular pain | |||
*Limited evidence for other conditions | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
[[Category:Pharmacology]] | |||
Revision as of 08:53, 25 June 2021
This article is still missing information.
Gabapentin
- First discovered in 1970s in an attempt to create a GABA analogue
- Whilst it resembles GABA, it does not act on the GABA receptor.
- Later discovered to act on α2δ subunits of voltage-dependent calcium channels to reduce calcium influx
- Precise mechanism of analgesia unclear
- Inhibits release of excitatory neurotransmitters: glutamate, NA, substance P
- Medsafe licenced for: neuropathic pain, adjunct anti-epileptic
- Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption: Saturable transporter so delayed peak levels at higher doses. Drugs that reduce motility (e.g opiates) increase bioavailability. Peak serum conc 3 hours
- Distribution: Less lipophilic so requires active transport across the BBB
- Metabolism: minimal
- Elimination: Renal excretion, half life 5-7 hours. Dose adjustment in renal impairment
Pregabalin
- Similar to gabapentin. Binds to α2δ subunits of voltage-dependent calcium channels to reduce calcium influx
- Inhibits release of excitatory neurotransmitters: glutamate, NA, substance P
- Medsafe licenced for: neuropathic pain, adjunct anti-epileptic
- Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption: Rapid absorption after oral administration. Peak serum conc 1h
- Distribution: Less lipophilic so requires active transport across the BBB
- Metabolism: minimal, no active metabolites
- Elimination: Renal excretion, half life 6.3 hours. Dose adjustment in renal impairment
Recommended prescribing: NZF
Gabapentin
- Day 1 300mg nocte
- Day 2 300mg bd
- Day 3 300mg tds
- Then increase by 300mg every 2-3 days to max dose 3600mg daily
Pregabalin
- Initially 75mg bd
- 150mg bd after 3-7 days
- Max dose 300mg bd after further 7 days
Titrate upwards until pain relief, side effects, or max dose reached
Remember to dose adjust for renal impairment: gabapentin if <80mL/min, pregabalin if <60mL/min
Caution in pregnancy (category B1); no clear data available, use if benefits outweigh risks
Evidence
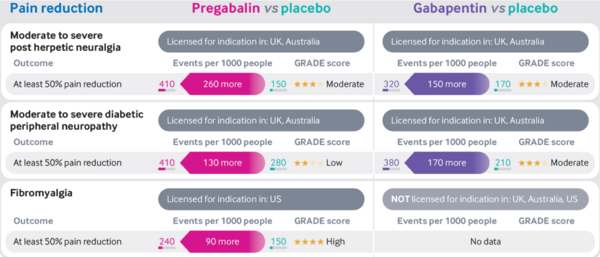
Post-herpetic neuralgia, diabetic peripheral neuropathy and fibromyalgia
- Moderate quality evidence supports the use of gabapentinoids to improve pain in those with post-herpetic neuralgia or diabetic peripheral neuropathy compared with placebo [1] [2]
- High quality evidence supports the use of pregabalin to improve pain in those with fibromyalgia compared to placebo [3]
- The evidence for gabapentin in fibromyalgia is unclear because of the small number of trials and very low quality of evidence available [4]
- NNTs
- Moderate to severe post-herpetic neuralgia: Pregabalin 4, Gabapentin 7
- Moderate to severe diabetic peripheral neuropathy: Pregabalin 8, Gabapentin 6
- Fibromyalgia: Gabapentin 10
Low back and radicular pain
- Systematic review and meta-analysis of 7 RCTs compared gabapentin and pregabalin to placebo. Judged moderate-high quality data [5]
- Low back pain with or without lumbar radicular pain
- No difference in pain or disability at short, intermediate or long term follow up
- Lumbar radicular pain only
- No difference in pain or disability at short, intermediate or long term follow up
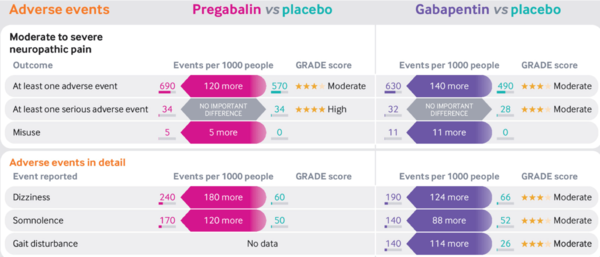
Adverse Effects
- Pregabalin and gabapentin similar profiles
- Dose-dependent
- No serious adverse effects c.f placebo
- Some common effects:
- Dizziness
- Somnolence
- Blurred vision
- Fatigue
- Weight gain and peripheral oedema
- Dry mouth
- Ataxia
- NNHs
- Moderate to severe neuropathic pain: Pregabalin 8, Gabapentin 7
Misuse and Abuse
- Supratherapeutic doses cause relaxation and euphoria.
- Taken in combination with other drugs e.g opiates, potentiates effect
- May assist with opioid withdrawal symptoms
- Those with a history of substance abuse (in particular opioids) at increased risk abuse
- UK survey: Lifetime prevalence of misuse 1.1% for gabapentin, 0.5% pregabalin
- Increasing death rate as per Finland, Sweden, Germany, UK post-mortem toxicology registers (almost all cases due to multisubstance)
- Misused gabapentinoids obtained from healthcare providers in 63% cases (UK and US study)
- In 2019, UK re-classified as scheduled class C drug (1 month prescriptions and no repeats)
- Think twice when prescribing and check indication if patient presents already on it[6]
Summary
- First line treatment for some patients with post-herpetic neuralgia and diabetic peripheral neuropathy
- Moderate to high quality evidence that not effective for low back pain or radicular pain
- Limited evidence for other conditions
References
- ↑ Derry et al.. Pregabalin for neuropathic pain in adults. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2019. 1:CD007076. PMID: 30673120. DOI. Full Text.
- ↑ Wiffen et al.. Gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain in adults. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2017. 6:CD007938. PMID: 28597471. DOI. Full Text.
- ↑ Derry et al.. Pregabalin for pain in fibromyalgia in adults. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2016. 9:CD011790. PMID: 27684492. DOI. Full Text.
- ↑ Cooper et al.. Gabapentin for fibromyalgia pain in adults. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2017. 1:CD012188. PMID: 28045473. DOI. Full Text.
- ↑ Enke et al.. Anticonvulsants in the treatment of low back pain and lumbar radicular pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. CMAJ : Canadian Medical Association journal = journal de l'Association medicale canadienne 2018. 190:E786-E793. PMID: 29970367. DOI. Full Text.
- ↑ Hägg, S et al. Current Evidence on Abuse and Misuse of Gabapentinoids. Drug Safety 2020.43, 1235–1254