◒
Supratrochlear Nerve Injection: Difference between revisions
From WikiMSK
No edit summary |
m (→See Also) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
* [[Auriculotemporal Nerve Injection]] | |||
* [[Greater Occipital Nerve Injection]] | |||
* [[Lesser Occipital Nerve Injection]] | |||
* [[Supraorbital Nerve Injection]] | |||
* [[TMJ Injection]] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| Line 33: | Line 37: | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Head | [[Category:Head and Jaw Procedures]] | ||
[[Category:Infoboxes]] | [[Category:Infoboxes]] | ||
[[Category:Partially complete articles]] | [[Category:Partially complete articles]] | ||
Latest revision as of 07:35, 7 March 2022
This article is still missing information.
| |
| Supratrochlear Nerve Injection | |
|---|---|
| Indication | Headache disorders and laceration repair |
| Syringe | 1-3mL |
| Needle | 27-30g |
Anatomy
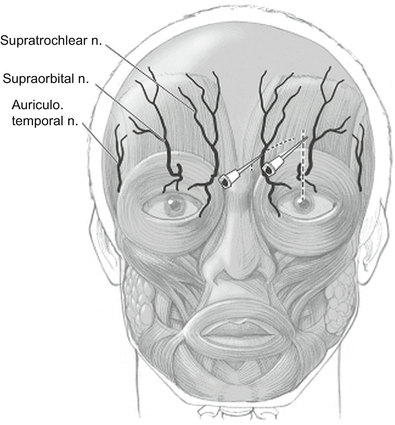
The supratrochlear nerve is a terminal cutaneous branch of the frontal nerve. The frontal nerve arises from the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve (V1). The supratrochlear nerve exits out from the orbital cavity and runs anterior and then ascends the forehead. It innervates the upper eyelid, forehead, and anterior scalp. The injection site is where it is found superficially at the superomedial aspect of the supraorbital ridge.
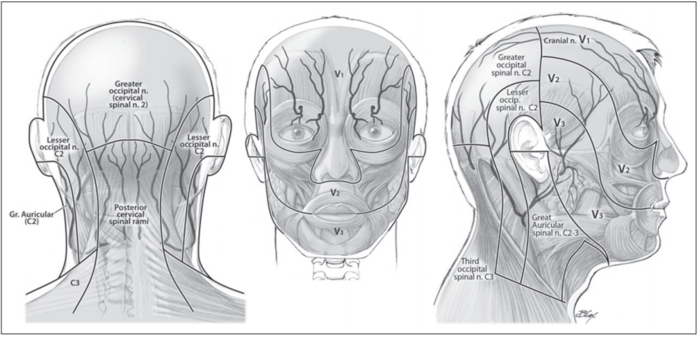
- Cranio-cervical Dermatomes.[1]
Technique
Landmark Guided
- Position the patient supine with their head in a neutral position.
- Use a 1.0 or 2.5 mL syringe with a 30-gauge needle.
- Locate the nasal bridge and the medial aspect of the supraorbital ridge.
- Insert the needle at the medial aspect of the corrugator muscle, just lateral to the procerus and above the eyebrow line to a depth of 4–5 mm.
- Aspirate to ensure not located in an artery and then inject, producing a small wheal under the skin
See Also
- Auriculotemporal Nerve Injection
- Greater Occipital Nerve Injection
- Lesser Occipital Nerve Injection
- Supraorbital Nerve Injection
- TMJ Injection
References
Literature Review
- Reviews from the last 7 years: review articles, free review articles, systematic reviews, meta-analyses, NCBI Bookshelf
- Articles from all years: PubMed search, Google Scholar search.
- TRIP Database: clinical publications about evidence-based medicine.
- Other Wikis: Radiopaedia, Wikipedia Search, Wikipedia I Feel Lucky, Orthobullets,