Trigger Finger Injection: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
|syringe=1mL | |syringe=1mL | ||
|needle=25-27G 16mm | |needle=25-27G 16mm | ||
|steroid= | |steroid=10mg triamcinolone | ||
|local=0.5mL 2% lidocaine or 0.5mL 0.25% | |local=0.5mL 2% lidocaine or 0.5mL 0.25% bupivacaine | ||
|volume=1mL | |volume=1mL | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
Landmark guidance has lower accuracy but equal efficacy to ultrasound guidance. Therefore landmark guidance is sufficient. There are four approaches to steroid injection and they are equally effective. The proximal phalanx injection approach is preferred due to its simplicity, safety, and tolerability.{{#pmid:32686570|Merry}} | Landmark guidance has lower accuracy but equal efficacy to ultrasound guidance. Therefore landmark guidance is sufficient. There are four approaches to steroid injection and they are equally effective. The proximal phalanx injection approach is preferred due to its simplicity, safety, and tolerability.{{#pmid:32686570|Merry}} | ||
=== | ===Conventional Method=== | ||
The classic method is injection into the superficial tendon sheath through the A1 pulley. The finger is then moved to ensure that the needle isn't in the tendon. | The classic method is injection into the superficial tendon sheath through the A1 pulley over the metacarpal head. The finger is then moved to ensure that the needle isn't in the tendon. Interestingly this technique has the needle in the sheath only 15% of the time, but is still effective. The downside is that it is painful for most patients.<ref name="Merry"/> | ||
===Modification of Classic Method=== | ===Modification of Classic Method=== | ||
A modification of the classic technique is injection extra-synovial superficial to the tendon sheath. | A modification of the classic technique is injection extra-synovial superficial to the tendon sheath.<ref name="Merry"/> | ||
===Lateral Approach=== | ===Lateral Approach=== | ||
The least painful technique is injection laterally into the proximal phalangeal portion of the tendon sheath. Care must be taken to avoid the neurovascular bundle. This technique is only suitable for those that perform the injection frequently due to higher difficulty. | The least painful technique is injection laterally into the proximal phalangeal portion of the tendon sheath. Care must be taken to avoid the neurovascular bundle. This technique is only suitable for those that perform the injection frequently due to higher difficulty.<ref name="Merry"/> | ||
===Proximal Phalanx Injection=== | ===Proximal Phalanx Intra-sheath Injection=== | ||
This method is simple, safe, and less painful than the classic technique. The injection is done over the palmar proximal phalanx, through the tendon, and into the posterior deep space between the tendon and sheath. Pain can be further reduced by initial subcutaneous digital block with 2mL of 1% lidocaine. | This method is simple, safe, and less painful than the classic technique. The injection is done over the palmar proximal phalanx, through the tendon, and into the posterior deep space between the tendon and sheath. Pain can be further reduced by initial subcutaneous digital block with 2mL of 1% lidocaine.<ref name="Merry"/> | ||
#After obtaining consent, position the patient with their hand supine on the procedure table. Ensure correct finger and mark with the tip of an ear speculum over the central proximal phalangeal flexor crease. | #After obtaining consent, position the patient with their hand supine on the procedure table. Ensure correct finger and mark with the tip of an ear speculum over the central proximal phalangeal flexor crease. | ||
#Clean the injection site | #Clean the injection site | ||
#Draw up a syringe with 0.5mL | #Draw up a syringe with 0.5mL bupivacaine 0.25% (or lidocaine) and 0.5mL methylprednisolone 40mg/mL. | ||
#Insert the 25-27g needle down into the target area. Pass the needle through the combined superficial and deep flexor tendon, and into the central volar proximal phalanx bone. Attempt injection. If there is no flow then withdraw the needle about 1mm to achieve flow into the space between the posterior flexor tendon sheath and the tendon. There is no need to confirm placement by moving the digit. For the thumb, the flexor tendon is less flat, and so the examiners non-dominant hand can grasp either side during injection into the ulnar/palmar side of the thumb over the proximal phalanx. | #Insert the 25-27g needle down into the target area . Pass the needle through the combined superficial and deep flexor tendon, and into the central volar proximal phalanx bone. Attempt injection. If there is no flow then withdraw the needle about 1mm to achieve flow into the space between the posterior flexor tendon sheath and the tendon. There is no need to confirm placement by moving the digit. For the thumb, the flexor tendon is less flat, and so the examiners non-dominant hand can grasp either side during injection into the ulnar/palmar side of the thumb over the proximal phalanx. | ||
<gallery mode=packed heights=200px> | |||
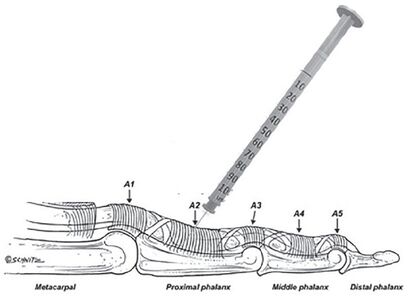
File:Proximal phalanx injection trigger finger anatomy.jpg|The digital pulley system and flexor tendon sheath injection at the proximal phalanx. | |||
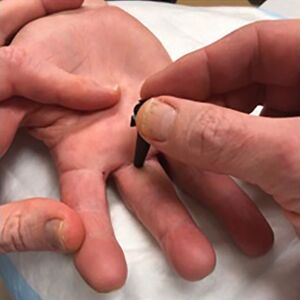
File:Proximal phalanx injection trigger finger marking target.jpg|Marking the target with the tip of an ear speculum. | |||
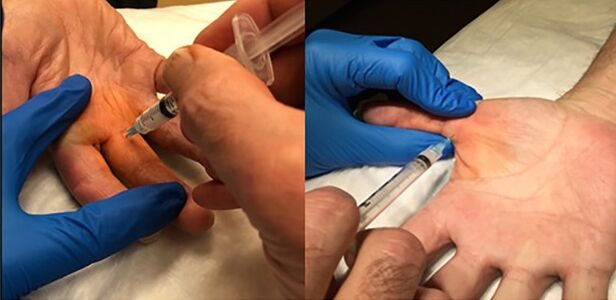
File:Proximal phalanx injection trigger finger.jpg|Proximal phalangeal intra-sheath injection technique. | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Complications== | ==Complications== | ||
Pain, bleeding, steroid flare reaction, infection, transient elevation of glucose levels in diabetes. Rare cases of tendon rupture and deep space infections. Rheumatoid arthritis confers a higher risk of tendon rupture and these patients should have surgical release.<ref name="Merry"/> | Pain, bleeding, steroid flare reaction, infection, transient elevation of glucose levels in diabetes. Rare cases of tendon rupture and deep space infections. Rheumatoid arthritis confers a higher risk of tendon rupture and these patients should have surgical release.<ref name="Merry"/> | ||
==Videos== | ==Videos== | ||
;Classic method | |||
<youtube>0VSxtk1oQ2s</youtube> | <youtube>0VSxtk1oQ2s</youtube> | ||
| Line 47: | Line 53: | ||
There should be discussion around future prevention such as using padded gloves, and decreasing the use of vibratory power tools that require tight gripping. | There should be discussion around future prevention such as using padded gloves, and decreasing the use of vibratory power tools that require tight gripping. | ||
Consider prescribing the use of a splint for 3 months post injection.<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Tajik|first=Hamidreza|last2=Shirzad|first2=Niloofar|last3=Rahimibarghani|first3=Sarvenaz|last4=Rezapour|first4=Bahare|last5=Nejadhosseinian|first5=Mohammad|last6=Faezi|first6=Seyedeh T.|last7=Fateh|first7=Hamid R.|date=2022-05-18|title=The effects of adding splint use to corticosteroid injection for the treatment of trigger finger: A randomized controlled trial|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35584268|journal=Musculoskeletal Care|doi=10.1002/msc.1647|issn=1557-0681|pmid=35584268}}</ref> | |||
Consider surgery if severe symptoms and failed trial of up to three injections.<ref name="Merry"/> | Consider surgery if severe symptoms and failed trial of up to three injections.<ref name="Merry"/> | ||
Latest revision as of 19:21, 22 January 2023
| Trigger Finger Injection | |
|---|---|
| Indication | Trigger Finger |
| Syringe | 1mL |
| Needle | 25-27G 16mm |
| Steroid | 10mg triamcinolone |
| Local | 0.5mL 2% lidocaine or 0.5mL 0.25% bupivacaine |
| Volume | 1mL |
For the treatment of Trigger Finger. Cure rates range between 60-90% for up to three injections.
Procedure
Landmark guidance has lower accuracy but equal efficacy to ultrasound guidance. Therefore landmark guidance is sufficient. There are four approaches to steroid injection and they are equally effective. The proximal phalanx injection approach is preferred due to its simplicity, safety, and tolerability.[1]
Conventional Method
The classic method is injection into the superficial tendon sheath through the A1 pulley over the metacarpal head. The finger is then moved to ensure that the needle isn't in the tendon. Interestingly this technique has the needle in the sheath only 15% of the time, but is still effective. The downside is that it is painful for most patients.[1]
Modification of Classic Method
A modification of the classic technique is injection extra-synovial superficial to the tendon sheath.[1]
Lateral Approach
The least painful technique is injection laterally into the proximal phalangeal portion of the tendon sheath. Care must be taken to avoid the neurovascular bundle. This technique is only suitable for those that perform the injection frequently due to higher difficulty.[1]
Proximal Phalanx Intra-sheath Injection
This method is simple, safe, and less painful than the classic technique. The injection is done over the palmar proximal phalanx, through the tendon, and into the posterior deep space between the tendon and sheath. Pain can be further reduced by initial subcutaneous digital block with 2mL of 1% lidocaine.[1]
- After obtaining consent, position the patient with their hand supine on the procedure table. Ensure correct finger and mark with the tip of an ear speculum over the central proximal phalangeal flexor crease.
- Clean the injection site
- Draw up a syringe with 0.5mL bupivacaine 0.25% (or lidocaine) and 0.5mL methylprednisolone 40mg/mL.
- Insert the 25-27g needle down into the target area . Pass the needle through the combined superficial and deep flexor tendon, and into the central volar proximal phalanx bone. Attempt injection. If there is no flow then withdraw the needle about 1mm to achieve flow into the space between the posterior flexor tendon sheath and the tendon. There is no need to confirm placement by moving the digit. For the thumb, the flexor tendon is less flat, and so the examiners non-dominant hand can grasp either side during injection into the ulnar/palmar side of the thumb over the proximal phalanx.
Complications
Pain, bleeding, steroid flare reaction, infection, transient elevation of glucose levels in diabetes. Rare cases of tendon rupture and deep space infections. Rheumatoid arthritis confers a higher risk of tendon rupture and these patients should have surgical release.[1]
Videos
- Classic method
Aftercare
Post-injection the patient should follow the "rule of 3s"
- Avoid using the finger for three days.
- Avoid tight grasping for three weeks
- Return for repeat injection in three months if no better, and then for a third and final injection after that.
The patient should expect improvement in pain in days, and improvement in locking and stiffness in weeks.
There should be discussion around future prevention such as using padded gloves, and decreasing the use of vibratory power tools that require tight gripping.
Consider prescribing the use of a splint for 3 months post injection.[2]
Consider surgery if severe symptoms and failed trial of up to three injections.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Merry et al.. Trigger Finger? Just Shoot!. Journal of primary care & community health 2020. 11:2150132720943345. PMID: 32686570. DOI. Full Text.
- ↑ Tajik, Hamidreza; Shirzad, Niloofar; Rahimibarghani, Sarvenaz; Rezapour, Bahare; Nejadhosseinian, Mohammad; Faezi, Seyedeh T.; Fateh, Hamid R. (2022-05-18). "The effects of adding splint use to corticosteroid injection for the treatment of trigger finger: A randomized controlled trial". Musculoskeletal Care. doi:10.1002/msc.1647. ISSN 1557-0681. PMID 35584268.
Literature Review
- Reviews from the last 7 years: review articles, free review articles, systematic reviews, meta-analyses, NCBI Bookshelf
- Articles from all years: PubMed search, Google Scholar search.
- TRIP Database: clinical publications about evidence-based medicine.
- Other Wikis: Radiopaedia, Wikipedia Search, Wikipedia I Feel Lucky, Orthobullets,