Basic Neurophysiology
Neurons are cells derived from the same embryonic tissue as skin, namely the ectoderm. They are highly differentiated epithelial cells. Their membranes have a unique abilty to transmit electrical signals. The function of the neuron is to provide a rapid transmission of information, which is often over large distances.
Terminology
Basic Structure
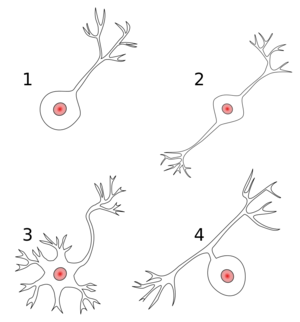
Motor Neuron and CNS Neurones
The nucleus is located in the cell body. Dendrites detect information to deliver to the cell. detect From the cell body is an extension of the membrane known as the axon that delivers information to a remote site. The axon terminal is called the telodendron.
Pseudounipolar Neurons - Sensory
In the peripheral nervous system, neurons have an analogous structure. In this situation, the cell body is offset from the axon. These cells are designed to reach out into the periphery to receive information. Their distal terminals have a receptor that detect stimuli from peripheral tissues, and is analogous to the dentrite. The axon refers to the entire conducting component of the cell, i.e. everything except the cell body.