Baxter's Nerve Entrapment
Baxter's nerve entrapment, also known as Baxter neuropathy, is plantar heel pain arising from compression of the inferior calcaneal nerve (Baxter nerve).
Anatomy
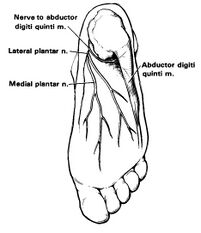
The inferior calcaneal nerve (Baxter nerve) is the first branch of the lateral plantar nerve, which is itself a branch of the tibial nerve. The nerve lies in between the abductor hallucis muscle and quadratus plantae.
The Gray's anatomy image and many other anatomy textbook images are incorrect. The Baxter nerve is quite posterior and lies very close to the calcaneus.
Classification
There are three entrapment points:
Tarsal tunnel syndrome is a related condition but involves entrapment more proximally in the tarsal tunnel.
Epidemiology and Risk Factors
Obesity, diabetes.
Clinical Features
The clinical features may be similar to or coexist with plantar fasciitis. However there may be less morning pain, occasional altered sensation, and intrinsic muscle atrophy.
Differential Diagnosis
- Plantar Fasciitis
- Fat Pad Contusion
- Calcaneal fractures (traumatic and stress)
- Inferior Calcaneal (Baxter) Nerve Entrapment
- Medial Calcaneal Nerve Entrapment
- Lateral Plantar Nerve Entrapment
- Medial Plantar Nerve Entrapment
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
- Lumbar Radicular Pain
- Talar stress fracture
- Retrocalcaneal bursitis
- Spondyloarthritis
- Osteoid osteoma
- CRPS
Treatment
Baxter's nerve Sd. Procedure: corticosteroid injection & orthotics. Good result. @Dr_Ramon_Balius #MSKUltrasound pic.twitter.com/ED9RcmqJnz
— Ramon Balius (@Dr_Ramon_Balius) March 21, 2016
References
- ↑ Baxter, D. E.; Thigpen, C. M. (1984-07). "Heel pain--operative results". Foot & Ankle. 5 (1): 16–25. doi:10.1177/107110078400500103. ISSN 0198-0211. PMID 6479759. Check date values in:
|date=(help)

