Proximal Weakness: Difference between revisions
m (→Classification) |
|||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
==Examination== | ==Examination== | ||
[[File:Gowers sign.jpg|thumb|right|Gower's sign from lying down. Can also be assessed from sitting.<ref name=":0" />]] | [[File:Gowers sign.jpg|thumb|right|Gower's sign from lying down. Can also be assessed from sitting.<ref name=":0" />|427x427px]] | ||
Gower's sign is a physical finding used to assess for proximal pelvic girdle muscle weakness particularly in those with certain [[Neuromuscular Disorders Overview|neuromuscular disorders]].<ref name=":0">Gowers. Pseudo-hypertrophic muscular paralysis : a clinical lecture. 1879. From https://archive.org/details/b21517034/page/n13/mode/2up</ref> | Gower's sign is a physical finding used to assess for proximal pelvic girdle muscle weakness particularly in those with certain [[Neuromuscular Disorders Overview|neuromuscular disorders]].<ref name=":0">Gowers. Pseudo-hypertrophic muscular paralysis : a clinical lecture. 1879. From https://archive.org/details/b21517034/page/n13/mode/2up</ref> | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
Assess for contractures, atrophy, and hypertrophy; seen in various disorders that cause proximal weakness. | Assess for contractures, atrophy, and hypertrophy; seen in various disorders that cause proximal weakness. | ||
== Investigations == | |||
[[File:EMG neuropathic vs myopathic.jpeg|left|thumb|EMG signals recorded from maximum muscle contraction.<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Wu|first=Yunfen|last2=Martnez Martnez|first2=Mara ngeles|last3=Orizaola Balaguer|first3=Pedro|date=2013-05-22|editor-last=Turker|editor-first=Dr.Hande|title=Overview of the Application of EMG Recording in the Diagnosis and Approach of Neurological Disorders|url=http://www.intechopen.com/books/electrodiagnosis-in-new-frontiers-of-clinical-research/overview-of-the-application-of-emg-recording-in-the-diagnosis-and-approach-of-neurological-disorders|language=en|publisher=InTech|doi=10.5772/56030|isbn=978-953-51-1118-4}}</ref>]] | |||
[[Electromyography]] can be particularly helpful in differentiating between myopathic and neuropathic causes. In a normal EMG trace, the electrical activity of a muscle appears as a smooth, regular pattern of muscle activation. In a neuropathic EMG trace, the electrical activity of the muscle appears abnormal, with irregular patterns of muscle activation. In a myopathic EMG trace, the electrical activity of the muscle appears increased and often shows signs of rapid firing or muscle fibre recruitment. | |||
== Resources == | == Resources == | ||
Revision as of 06:26, 10 March 2023
Classification
| Proximal Weakness | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Myopathic | Non-Myopathic | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Acquired | Genetic | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Examination
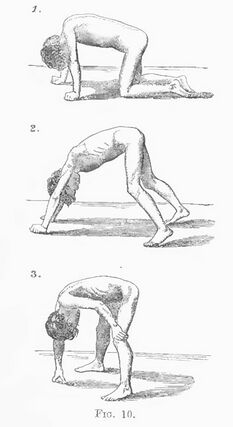
Gower's sign is a physical finding used to assess for proximal pelvic girdle muscle weakness particularly in those with certain neuromuscular disorders.[1]
To perform the Gower's sign test, the patient is asked to rise from a sitting or lying position on the floor without using their hands or arms for support. Patients with normal muscle strength are able to perform this task with ease. However, patients with proximal lower limb muscle may use their hands and arms to "climb up" their own body, pushing against their thighs, hips, and abdomen to achieve a standing position. This maneuver is often accompanied by compensatory movements, such as hyperextension of the knees or lordosis of the lumbar spine.
For the upper limbs there may be scapular winging and difficulty in abduction.
Assess for contractures, atrophy, and hypertrophy; seen in various disorders that cause proximal weakness.
Investigations
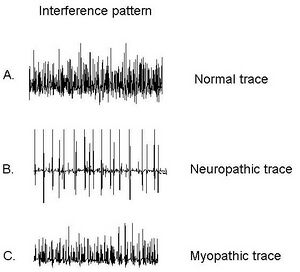
Electromyography can be particularly helpful in differentiating between myopathic and neuropathic causes. In a normal EMG trace, the electrical activity of a muscle appears as a smooth, regular pattern of muscle activation. In a neuropathic EMG trace, the electrical activity of the muscle appears abnormal, with irregular patterns of muscle activation. In a myopathic EMG trace, the electrical activity of the muscle appears increased and often shows signs of rapid firing or muscle fibre recruitment.
Resources
EURO-NMD Lecture on Proximal Weakness
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Gowers. Pseudo-hypertrophic muscular paralysis : a clinical lecture. 1879. From https://archive.org/details/b21517034/page/n13/mode/2up
- ↑ Wu, Yunfen; Martnez Martnez, Mara ngeles; Orizaola Balaguer, Pedro (2013-05-22). Turker, Dr.Hande (ed.). "Overview of the Application of EMG Recording in the Diagnosis and Approach of Neurological Disorders" (in English). InTech. doi:10.5772/56030. ISBN 978-953-51-1118-4. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help)

