◔
Proximal Weakness
From WikiMSK
This article is a stub.
Classification
| Proximal Weakness | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Myopathic | Non-Myopathic | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Acquired | Genetic | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Examination
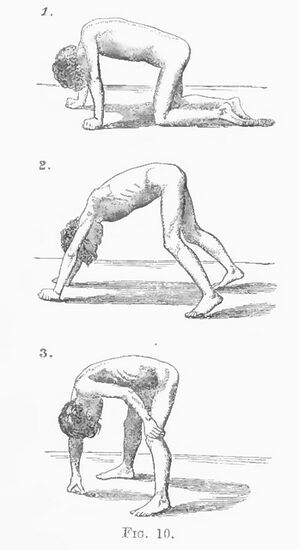
Gower's sign.[1]
Gower's sign is a physical finding used to assess for proximal lower limb muscle weakness particularly in those with certain neuromuscular disorders.[1]
To perform the Gower's sign test, the patient is asked to rise from a sitting or lying position on the floor without using their hands or arms for support. Patients with normal muscle strength are able to perform this task with ease. However, patients with proximal lower limb muscle may use their hands and arms to "climb up" their own body, pushing against their thighs, hips, and abdomen to achieve a standing position. This maneuver is often accompanied by compensatory movements, such as hyperextension of the knees or lordosis of the lumbar spine.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Gowers. Pseudo-hypertrophic muscular paralysis : a clinical lecture. 1879. From https://archive.org/details/b21517034/page/n13/mode/2up

