Sagittal Band Injuries: Difference between revisions
m (→Imaging) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Stub}} | {{Stub}} | ||
Sagittal band injuries | Sagittal band injuries (also known as Boxer's knuckle, not to be confused with Boxer's fracture) results from acute direct trauma or chronic, repetitive microtrauma, and typically occur in boxers. | ||
== | == Anatomy == | ||
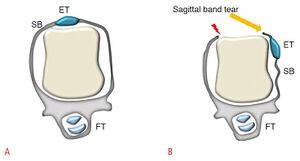
[[File:Sagittal band tear.jpg|thumb|'''A:''' Intact sagittal band'''B: S'''agittal band tear with subluxation of extensor tendon | [[File:Sagittal band tear.jpg|thumb|'''A:''' Intact sagittal band'''B: S'''agittal band tear with subluxation of extensor tendon | ||
ET: extensor tendon; FR: flexor tendon; SB: sagittal band.]] | ET: extensor tendon; FR: flexor tendon; SB: sagittal band.]] | ||
At the dorsal aspect of the MCPJ the extensor tendons are stabilised by the extensor hood and particularly by the sagittal band during flexion and extension of the fingers. | At the dorsal aspect of the MCPJ the extensor tendons are stabilised by the extensor hood and particularly by the sagittal band during flexion and extension of the fingers. The ulnar and radial sagittal bands exert tensile forces in opposite directions during flexion, which keeps the extensor tendon in apposition with the metacarpal bone. | ||
== Pathology == | |||
Since the sagittal band prevents deviation of the extensor tendon during flexion and bowstringing during MCP joint hyperextension, injury to the sagittal band causes extensor tendon dislocation. | Since the sagittal band prevents deviation of the extensor tendon during flexion and bowstringing during MCP joint hyperextension, injury to the sagittal band causes extensor tendon dislocation. | ||
| Line 14: | Line 15: | ||
== Clinical Features == | == Clinical Features == | ||
[[File:Sagittal band tear extensor tendon subluxation.mp4|thumb|right|Extensor tendon dislocation during flexion]]The sagittal band prevents deviation of the extensor tendon during MCPJ flexion and bowstringing during hyperextension. Therefore extensor tendon dislocation can be observed during flexion. | [[File:Sagittal band tear extensor tendon subluxation.mp4|thumb|right|Extensor tendon dislocation during flexion]]History is often of the patient punching an object with a clenched fist. Less often it can occur in non-traumatic situations such as in Rheumatoid Arthritis. | ||
The sagittal band prevents deviation of the extensor tendon during MCPJ flexion and bowstringing during hyperextension. Therefore extensor tendon dislocation can be observed during flexion. | |||
== Imaging == | == Imaging == | ||
[[File:Sagittal band tear ultrasound.jpg|thumb|Sagittal band tear in a 43-year-old woman. '''A''': Transverse view of the 3rd MCPJ with finger extended. Abnormal radial sagittal band shown with irregularity and hypoechogenicity (arrow). The extensor tendon (asterix) is positioned normally. | [[File:Sagittal band tear ultrasound.jpg|thumb|Sagittal band tear in a 43-year-old woman. '''A''': Transverse view of the 3rd MCPJ with finger extended. Abnormal radial sagittal band shown with irregularity and hypoechogenicity (arrow). The extensor tendon (asterix) is positioned normally. | ||
Revision as of 12:40, 6 February 2022
Sagittal band injuries (also known as Boxer's knuckle, not to be confused with Boxer's fracture) results from acute direct trauma or chronic, repetitive microtrauma, and typically occur in boxers.
Anatomy
At the dorsal aspect of the MCPJ the extensor tendons are stabilised by the extensor hood and particularly by the sagittal band during flexion and extension of the fingers. The ulnar and radial sagittal bands exert tensile forces in opposite directions during flexion, which keeps the extensor tendon in apposition with the metacarpal bone.
Pathology
Since the sagittal band prevents deviation of the extensor tendon during flexion and bowstringing during MCP joint hyperextension, injury to the sagittal band causes extensor tendon dislocation.
The most frequent location of this injury is the third finger. The site of the tear may affect whether the extensor tendon is displaced towards the radial or ulnar side. Although the most frequent site of disruption is the radial sagittal band, such that the extensor tendon dislocates in an ulnar direction, radial subluxation can occur with forced valgus injury. Since the second and fifth fingers have two tendons per finger, they may displace in different directions, one to the radial side and the other to the ulnar side.
Clinical Features
History is often of the patient punching an object with a clenched fist. Less often it can occur in non-traumatic situations such as in Rheumatoid Arthritis.
The sagittal band prevents deviation of the extensor tendon during MCPJ flexion and bowstringing during hyperextension. Therefore extensor tendon dislocation can be observed during flexion.
Imaging
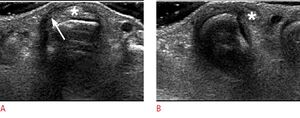
Ultrasound demonstrates irregular thickening of the abnormal sagittal band with hypoechogenicity. The extensor tendon can appear normal or can become swollen with loss of the fibrillar pattern, suggestive of a partial tear. On dynamic examination, the extensor tendon can be subluxed or dislocated during finger flexion in the transverse plane.
References
Part or all of this article or section is derived from Current status of ultrasonography of the finger by Seun Ah Lee et al, used under CC-BY-NC