Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is caused by compression of the brachial plexus or subclavian vessels as they pass through the narrow passageways leading from the base of the neck to the axilla and arm. There is considerable disagreement about its diagnosis and treatment, particularly the neurogenic form.
Anatomy
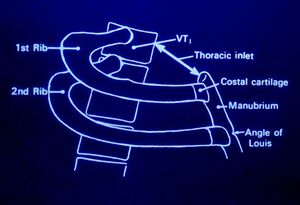
The thoracic outlet is found at the base of the neck. It consists of the first rib and adjacent structures. The upper thoracic aperture is bordered by:
- Posteriorly - spine
- Anteriorly - manubrium
- Laterally - 1st rib
The stellate ganglion sits posterior to the subclavian artery. It is anterior to the 1st rib, transverse process of C7, and the anterior primary rami of C8 and T1. It receives white rami communicantes from C8 and T1 (afferent sympathetic fibres from the brachial plexus and upper intercostal nerves). It sends grey rami communicantes to C8 and T1 (efferent sympathetic fibres to brachial plexus and intercostal nerves)
Pathophysiology
Thoracic outlet syndrome is caused by an enlargement or change of the tissues in or near the thoracic outlet leading to neurovascular compression.
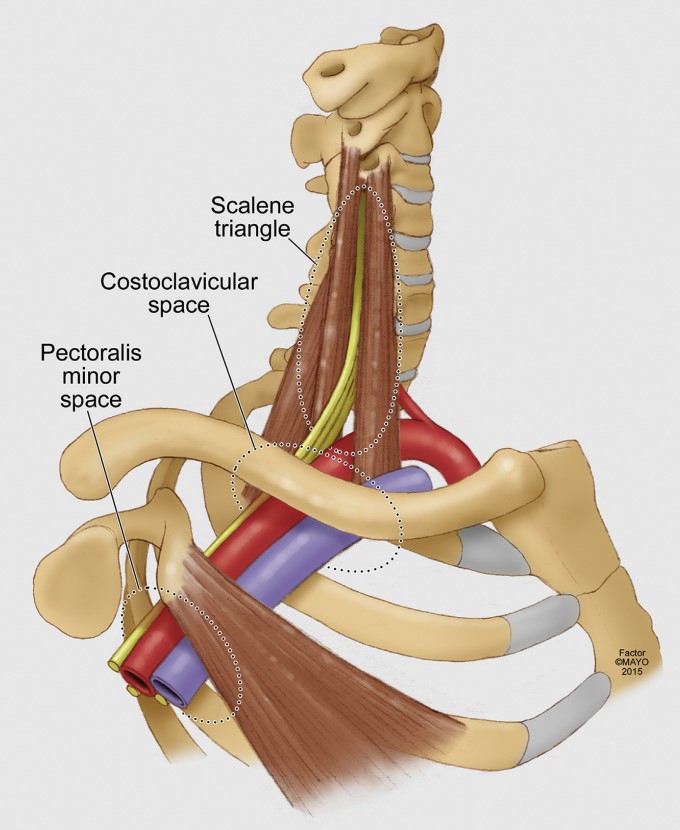
Neurovascular compression can occur at three different anatomic levels
- Interscalene triangle (between the scalene muscles)
- Costoclavicular space (between the first rib and clavicle)
- Pectoralis minor space (under the pectoralis minor)
NTOS: brachial plexus compression can occur at the interscalenne triangle or the pectoralis minor space.
VTOS: Venous compression occurs most commonly at the costoclavicular space, but can occasionally occur at the pectoralis minor space.
ATOS: Arterial compression occurs most commonly at the scalene triangle typically by an anomalous bone or ligamentous structure.[1]
Various causes have been proposed including
- Anomalous scalene bands. fibrous band may extend from the tip of the abnormal transverse process to the first rib.
- Anomaly or fracture of 1st rib
- Cervical rib
- Fracture clavicle
- 1st rib dysfunction. Subluxation cranially at the costotransverse joint leading to irritation of the nerve roots C8 and T1 as well as the stellate ganglion.
- Myofascial dysfunction and pain (scalenes, pectoralis minor, infraspinatus, teres minor). Restriction of internal rotation can be seen, this may be due to the fact that the axillary nerve C5/6 comes off the posterior cord (teres minor and deltoid)
- Tumour
- Repetitive trauma
- Stellate ganglion irritation causing autonomic symptoms/signs.
Often there is no direct cause.
Note that anomalies of the thoracic outlet are also common in asymptomatic individuals. In a study of 50 cadavers only 10% had a bilaterally normal anatomy.[2]
Classification
Thoracic outlet syndrome is divided into:[1]
- Neurogenic (ATOS): Caused by compression of the inferior trunk of the brachial plexus due to a cervical rib, band, or enlarged scalenus muscles.
- NPMS: Neurogenic pectoralis minor syndrome is a subgroup with compression at the pectoralis minor space. If limited to the scalene triangle it is called NTOS. It combined then it is called NTOS/NPMS.
- Arterial Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (NTOS): Caused by objective compression of the subclavian artery at the interscalene triangle.
- Venous Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (VTOS): Caused by compression of the subclavian vein at the costoclavicular junction, or occasionally at the pectoralis minor space.
- Paget-Schroetter syndrome: thrombotic occlusion at the costoclavicular junction, also called effort thrombosis
- McCleeery syndrome: intermittent positional obstruction in the absence of thrombosis
- VPMS: subgroup where the compression is limited to the pectoralis minor space. If limited to the costoclavicular junction it is called VTOS. If combined it is called VTOS/VPMS.
- Persistent TOS: Of any type, means that it hasn't improved after treatment
- Recurrent TOS: Symptoms have recurred after an initial three month period of improvement.
- Secondary TOS: Symptoms of a different type have occurred after treatment of a different problem.
The following terms should not be used: True, disputed, or nonspecific NTOS, vascular TOS, mixed TOS, Roos classification.
Epidemiology
The condition is more common in women. The onset of symptoms usually occurs between 20 and 50 years of age
Clinical Features
History
Pain: Pain is dull and aching in nature and may occur in the shoulder and upper arm, chest, axilla, and neck. The pain may radiate distally to the medial arm, lateral shoulder, and dorsal forearm. Pain can occur at night.
General: Symptoms are worse when working with the arm above horizontal.
NTOS: Numbness and paraesthesias of the arm usually the medial arm and hand (4th and 5th fingers). There may be weakness in the shoulders, arm, and hands. Arterial signs and symptoms can be present in patients with NTOS. However ATOS is not diagnosis unless there is proven symptomatic ischaemia. VTOS is less commonly seen in conjunction with NTOS.
VTOS: Presents as acute or chronic upper extremity deep venous thrombosis (Paget-Schroetter syndrome, effort thrombosis), or positional swelling (McCleery syndrome)
ATOS: Presents as either symptomatic ischaemia with arm elevation or fixed arterial injury (stenosis, occlusion, or aneurysm).
Examination
There may be tenderness in the supraclavicular area, weakness and/or paraesthesias with arm elevation, pallor of the palm with arm elevation and fingers pointing to the ceiling, and weakness of the 5th finger.
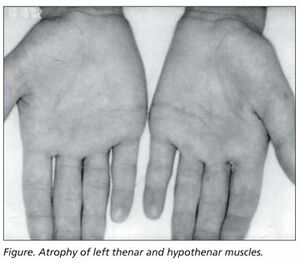
In neurogenic thoracic outlet syndrome the patient may have the Gilliat-Sumner hand in which there is severe wasting in the fleshy base of the thumb. Atrophy of abductor pollicis brevis may mimic Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.
CRPS like signs can occur with stellate ganglion compression such as swelling of the extremities and fingers.
The first rib should be examined. The patient is seated as for examination of the cervical spine. Lateral flexion is tested bilaterally. With the head in lateral flexion, the supraclavicular area on the side of flexion is palpated. The first rib is located medially in the supraclavicular area. The patient is asked to breathe in, and the first rib rises against the pressure of the examining finger. Pain may be elicited locally. Paraesthesiae in the C8 or T1 areas may be reported.
There may be restricted abduction and internal rotation of the ipsilateral shoulder.
There are a variety of special tests (Table 1)
| Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Tests | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test | Sensitivity | Specificity | +LR | -LR | Kappa |
| Cervical Rotation Lateral Flexion Test[4] | 0.92 | 0.90 | 9.2 | 0.09 | 1.0 |
| Both Adson + Wright (pulse) positive | 0.54 | 0.94 | 9.0 | 0.5 | |
| Both Adson + hyperabduction (sx) positive | 0.72 | 0.88 | 6 | 0.3 | |
| Hyperabduction (pulse abolition) | 0.52 | 0.90 | 5.2 | 0.5 | |
| Both Adson + Roos positive | 0.72 | 0.82 | 4 | 0.3 | |
| Both Adson + Wright (sx) positive | 0.79 | 0.76 | 3.3 | 0.3 | |
| Both Adson + Roos positive | 0.72 | 0.82 | 4 | 0.3 | |
| Adson test | 0.79 | 0.76 | 3.3 | 0.3 | |
| Tinel sign | 0.86 | 0.56 | 2.0 | 0.3 | |
| Both Wright (pulse) + hyperabduction (sx) positive | 0.63 | 0.69 | 2.0 | 0.5 | |
| Both Wright (sx) + hyperabduction (sx) positive | 0.83 | 0.50 | 1.7 | 0.3 | |
| Both Wright (sx) + Roos positive | 0.83 | 0.47 | 1.6 | 0.4 | |
| Wright test (pulse abolition) | 0.70 | 0.53 | 1.5 | 0.6 | |
| Hyperabduction (sx reproduction) | 0.84 | 0.40 | 1.4 | 0.4 | |
| Wright test (sx reproduction) | 0.90 | 0.29 | 1.3 | 0.3 | |
| Roos test | 0.84 | 0.30 | 1.2 | 0.5 | |
Investigations
Electrophysiological tests are typically normal below the clavicle. However in some cases there may be the following findings in classic neurogenic TOS:
- Low compound muscle action potential in the thenar and intrinsic muscles
- Abnormal sensory nerve conduction in the ulnar nerve
- Prolonged F-wave latency in the ulnar nerve
- Abnormal medial antebrachial cutaneous sensory nerve conduction)
Plain films can be used to assess for an extra cervical rib
Venous and arterial anatomy can be assessed by catheter angiography, doppler, or MR angiography and venography.
Differential Diagnosis
- Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy
- Cervical disc disorders
- C7 or C8 nerve root compression
- Ulnar neuropathy
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Fibromyalgia
- Multiple Sclerosis
- CRPS
- Neuralgic Amyotrophy
- Syringomyelia
Diagnosis
NTOS: The diagnosis of NTOS can be made when three of the following four criteria are present:[1]
- LOCAL FINDINGS:
- History: Symptoms consistent with irritation or inflammation at the site of compression (scalene triangle for NTOS, and pectoralis insertion for NPMS), plus symptoms due to referred pain. Patients may have pain in the chest, axilla, upper back, shoulder, trapezius, neck, or head.
- Examination: Tenderness of the affected area.
- PERIPHERAL FINDINGS:
- History: Arm or hand symptoms consistent with proximal nerve compression. Symptoms include numbness, pain, paraesthesias, vasomotor changes, and weakness. Muscle wasting can occur in extreme. Symptoms are exacerbated by movements that either narrow the thoracic outlet (lifting arms overhead) or stretch the brachial plexus (dangling, driving, walking/running).
- Examination: Reproduction of peripheral symptoms with palpation of the affected area (scalene triangle or pectoralis minor insertion site). The EAST or ULTT test may provoke symptoms.
- ABSENT FINDINGS:
- Cervical disc disease, shoulder disease, carpal tunnel syndrome, chronic regional pain syndrome, brachial neuritis.
- INJECTION:
- Response to a properly performed test injection
Treatment
Nonsurgical treatment
Malfunction of the first rib: isometric contraction of scalenus anterior and medius results in elevation of the first rib anteriorly, and reduces posterior subluxation. The therapist places their hand over the lateral head with the patient in a seated position. The patient contracts against the therapists hand. Gentle mobilisations are done over 20 seconds.
Postural dysfunction: Spinal postural stability; release tight pectoralis minor (pec minor may be tight without 1st rib dysfunction with arm elevation), scalene and shoulder girdle muscles (e.g. infraspinatus and teres minor); maintain cervicothoracic mobility; strengthen scapula muscles, lower and middle trapezius, and serratus anterior; strengthen rotator cuff; address ergonomic factors; address work behaviour factors.
Injections:
See Also
Reporting standards are by Illig et al. [1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Illig et al.. Reporting standards of the Society for Vascular Surgery for thoracic outlet syndrome. Journal of vascular surgery 2016. 64:e23-35. PMID: 27565607. DOI.
- ↑ Juvonen T, Satta J, Laitala P, Luukkonen K, Nissinen J. Anomalies at the thoracic outlet are frequent in the general population. Am J Surg. 1995 Jul;170(1):33-7. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(99)80248-7. PMID: 7793491.
- ↑ Gillard et al.. Diagnosing thoracic outlet syndrome: contribution of provocative tests, ultrasonography, electrophysiology, and helical computed tomography in 48 patients. Joint bone spine 2001. 68:416-24. PMID: 11707008. DOI.
- ↑ Lindgren KA, Leino E, Manninen H. Cervical rotation lateral flexion test in brachialgia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1992 Aug;73(8):735-7. PMID: 1642524.
Literature Review
- Reviews from the last 7 years: review articles, free review articles, systematic reviews, meta-analyses, NCBI Bookshelf
- Articles from all years: PubMed search, Google Scholar search.
- TRIP Database: clinical publications about evidence-based medicine.
- Other Wikis: Radiopaedia, Wikipedia Search, Wikipedia I Feel Lucky, Orthobullets,