◔
Ilioinguinal Nerve: Difference between revisions
From WikiMSK
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
|innervates=Inferior abdominal muscles, skin to inguinal region, small area of medial thigh, upper scrotum/labia. | |innervates=Inferior abdominal muscles, skin to inguinal region, small area of medial thigh, upper scrotum/labia. | ||
}} | }} | ||
==Innervation of the Perineum== | |||
[[File:Perineum innervation Trescot.png|thumb|left|350px|Innervation of the perineum: A: [[Genitofemoral Nerve|genitofemoral nerve]]; B: [[Obturator Nerve|obturator nerve]]; C: [[Inferior Cluneal Nerve|inferior cluneal nerve]]; D: perineal branch of the [[Posterior Femoral Cutaneous Nerve|posterior femoral cutaneous nerve]]; E: [[Ilioinguinal Nerve|ilioinguinal nerve]]; F: [[Pudendal Nerve|pudendal nerve]]<br><small>Copyright Andrea Trescot<ref name="trescot">Trescot, Andrea. Peripheral nerve entrapments : clinical diagnosis and management. Switzerland: Springer, 2016.</ref></small>]] | |||
{{Nerves of the lumbosacral plexus|state=collapsed}} | {{Nerves of the lumbosacral plexus|state=collapsed}} | ||
==References== | |||
Revision as of 15:29, 9 April 2022
This article is a stub.
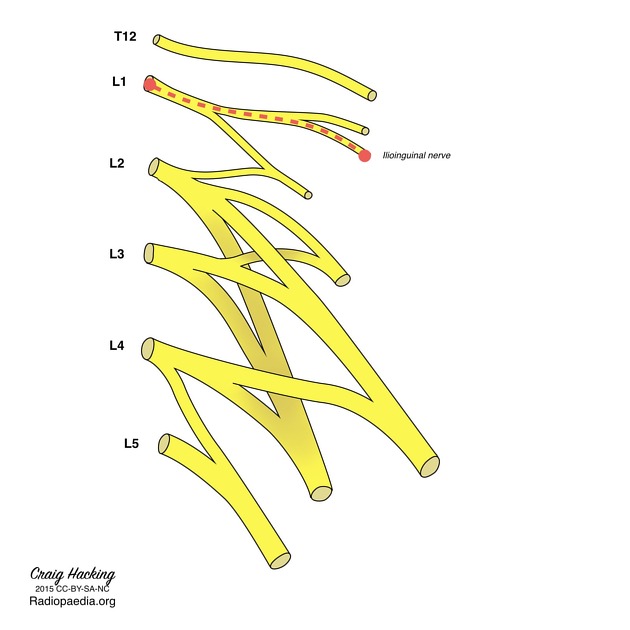
| |
| Ilioinguinal Nerve | |
|---|---|
| Nerve Type | Mixed nerve |
| Origin | L1 |
| Sensory innervation | Skin to inguinal region, small area of medial thigh, upper scrotum/labia. |
| Motor innervation | Inferior abdominal muscles |
Innervation of the Perineum
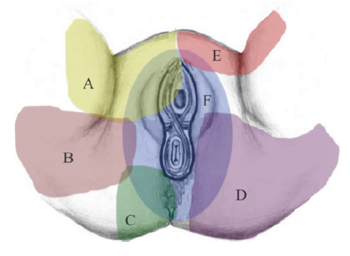
Innervation of the perineum: A: genitofemoral nerve; B: obturator nerve; C: inferior cluneal nerve; D: perineal branch of the posterior femoral cutaneous nerve; E: ilioinguinal nerve; F: pudendal nerve
Copyright Andrea Trescot[1]
Copyright Andrea Trescot[1]
References
- ↑ Trescot, Andrea. Peripheral nerve entrapments : clinical diagnosis and management. Switzerland: Springer, 2016.

