Tibial Nerve: Difference between revisions
From WikiMSK
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
|motorinnervates=[[Posterior Compartment of the Thigh]], [[Posterior Compartment of the Leg]], muscles of the sole of the foot | |motorinnervates=[[Posterior Compartment of the Thigh]], [[Posterior Compartment of the Leg]], muscles of the sole of the foot | ||
}} | }} | ||
==Lesion Effect== | |||
A high lesion of the tibial nerve results in | |||
*Loss of flexion of the toes and inversion of the foot. | |||
*Loss of sensation of the sole of the foot, inferior aspect of the toes, and nail beds | |||
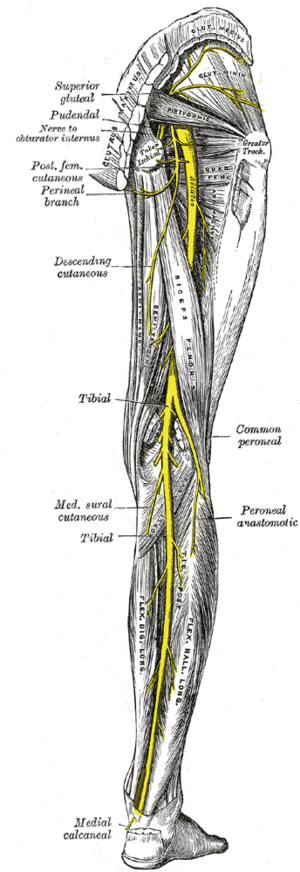
[[File:Posterior leg nerves Gray832.png|thumb|right|Nerves of the right lower limb, posterior view]] | [[File:Posterior leg nerves Gray832.png|thumb|right|Nerves of the right lower limb, posterior view]] | ||
{{Nerves of the lumbosacral plexus|state=collapsed}} | {{Nerves of the lumbosacral plexus|state=collapsed}} | ||
Revision as of 08:26, 18 April 2022
| |
| Tibial Nerve | |
|---|---|
| Nerve Type | Mixed nerve |
| Origin | One of the two branches of the sciatic nerve in the lower third of the thigh. L4-S3. |
| Course | Through popliteal fossa, deep to gastrocnemius, and under the flexor retinaculum of the ankle. |
| Major Branches | Sural Nerve, Medial Plantar Nerve, Lateral Plantar Nerve, Medial Calcaneal Nerve |
| Sensory innervation | Articular branches to the joints of the knee, ankle, and foot. Cutaneous branches to the posterior calf and sole of the foot. |
| Motor innervation | Posterior Compartment of the Thigh, Posterior Compartment of the Leg, muscles of the sole of the foot |
Lesion Effect
A high lesion of the tibial nerve results in
- Loss of flexion of the toes and inversion of the foot.
- Loss of sensation of the sole of the foot, inferior aspect of the toes, and nail beds