⬤
Planar Joint: Difference between revisions
From WikiMSK
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== List of {{PAGENAME}}s == | == List of {{PAGENAME}}s == | ||
{{Not ported}}{{#ask: | {{Not ported}}{{#ask: | ||
[[Has joint type::Planar Joint]] | [[Has joint secondary type::Planar Joint]] | ||
|?Has joint bones=Bones | |?Has joint bones=Bones | ||
|?Has joint ligaments=Ligaments | |?Has joint ligaments=Ligaments | ||
Revision as of 09:16, 2 April 2022
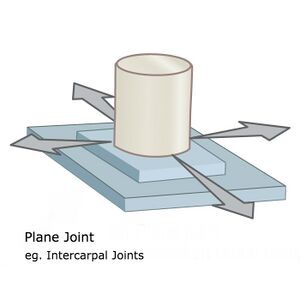
A planar joint, or gliding joint, is defined as an articulation between bones that are both flat and of similar size. This type of joint is multiaxial because it permits many movements; however, surrounding ligaments usually restrict this joint to a small and tight motion. Examples include intercarpal joints, intertarsal joints, and the acromioclavicular joint.[1]
List of Planar Joints
- This section is original unported content
| Synovial Joint | Bones | Ligaments | Muscles | Innervation | Vasculature | ROM | Volume |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acromioclavicular Joint | Clavicle Scapula | Coracoclavicular, coracoacromial, superior acromioclavicular, and inferior acromioclavicular ligaments. | No muscles directly act on this joint. | Axillary, suprascapular, and lateral pectoral nerves | Suprascapular and thoracoacromial arteries | Upward rotation: 30 degrees, external rotation:8 degrees | 2mL |
| Cervical Zygapophyseal (Facet) Joint | |||||||
| Lumbar Zygapophyseal (Facet) Joint | Vertebra | Capsular Ligament | Medial Branches of the Dorsal Rami | Branches of Lumbar Arteries | Limited Flexion, Extension, Lateral Flexion, and Rotation | ||
| Talocalcaneal Joint (Subtalar Joint) | Talus Calcaneus | Multiple, interosseous talocalcaneal ligament is most important | Medial plantar, lateral plantar, and deep fibular nerves | Posterior tibial and fibular arteries | Equal components of inversion/eversion and abduction/adduction. |
References
- ↑ Juneja, Pallavi; Munjal, Akul; Hubbard, John B. (2022). "Anatomy, Joints". Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. PMID 29939670. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help)